Knowledge
Enterprise Knowledge Base is a tool for centralized storage and management of information and knowledge within an organization. It helps enterprises effectively organize, store, retrieve and share various types of information and knowledge resources, and provides a foundation for enterprise-specific AI applications. Through layout recognition, text splitter, vectorization technology, semantic retrieval, etc., a large amount of data within the enterprise can be effectively processed and utilized, which can not only improve the performance of large models on specific tasks, but also greatly reduce the consumption of computing resources and improve the efficiency and accuracy of data processing.
In enterprise applications, the knowledge reserve of large models is expanded by mounting private knowledge bases (mounting is achieved through retrieval enhancement generation technology/RAG, which allows large models to understand, summarize, organize and answer questions, making large language models more practical and credible in actual applications), so as to provide natural language-based, conversational enterprise private knowledge access, and solve the illusion problem caused by insufficient domain knowledge of general large models when facing enterprise applications. After mounting the enterprise knowledge base, the enterprise knowledge base documents and data are stored in the vector database after vector feature extraction (embedding), and apply LLM and vectorized knowledge base to search and compare knowledge to build intelligent applications. You can choose to mount the enterprise knowledge base when orchestrating applications in Application-My applications to facilitate AI applications to answer questions based on knowledge base files (see: Create AI Application).
Data-Knowledge displays all knowledge bases and knowledge base directories created by users under the same tenant, along with the number of associated applications. Users can only maintain knowledge bases or directories for which they have permissions, including those they created and those authorized by others. Click the "Create Knowledge Base" button in the upper left corner to create a new enterprise knowledge base (supports two methods: ① Create platform knowledge base. ② Synchronize external data sources. ) Successfully created enterprise knowledge bases will be displayed in Data-Knowledge.
Additionally, users can view detailed conversation logs in the Log Monitoring. Based on user feedback, they can use “Record QA” to select real Q&A pairs from conversation logs, edit and correct them, and feed them back into the knowledge base (see: Application log monitoring,enabling quick correction and accuracy improvement.
Create Knowledge Base
Create platform knowledge base
Introduction
The core principles of creating an enterprise knowledge base and conducting knowledge governance through the "Create Platform Knowledge Base" are as follows:
Layout Recognition: The core lies in the precise analysis of document layout. Through advanced algorithms/models, layout recognition technology can accurately identify elements such as text, images, tables, etc. in documents, and store and display the parsed elements and key information in a structured manner.
Chunk Settings: Split the knowledge in the knowledge base. You can choose between automatic Chunk or custom Chunk (Custom parameters and rule parameters as needed).
- Automatic:
- Local unstructured documents: Intelligently identify document content, ensuring the integrity of structure and semantics, with a maximum chunk length of 1024 characters.
- Table: The \n Chunk mode is used, and each row of data will be saved as a chunk.
- Local FAQ: The FAQ Chunk mode is used.
- Website: Intelligently identify document content, ensuring the integrity of structure and semantics, with a maximum chunk length of 1024 characters.
- Custom: Custom parameters such as chunk rules, chunk length, and preprocessing rules. Applicable to unstructured documents (including websites).
- Automatic: Based on the Automatic Chunk, users can set maximum chunk length. (range:200-1,000)
- Linefeed: Based on the Automatic Chunk, users can use linefeed to splitNote. Suitable for plain text. Not effective for file Layout-Recognized.
- Double Linefeed: Based on the Automatic Chunk, users can use double linefeed to splitNote. It is recommended to set a larger maximum segment length to keep segment content complete. Not effective for file Layout-Recognized.
- Custom: Based on the Automatic Chunk, users can define their own custom delimiters and set the maximum segment length. Custom delimiters are only as split signals and are not retained in the final segments. For example:===******===,===delimiters==。Not effective for file Layout-Recognized.
- Associate information:
- Associate file name: Automatically add a reference to the file name at the beginning of each segment.
- Associate titles and subtitles: Supplement each segment with its title and subtitle for context.
- Automatic:
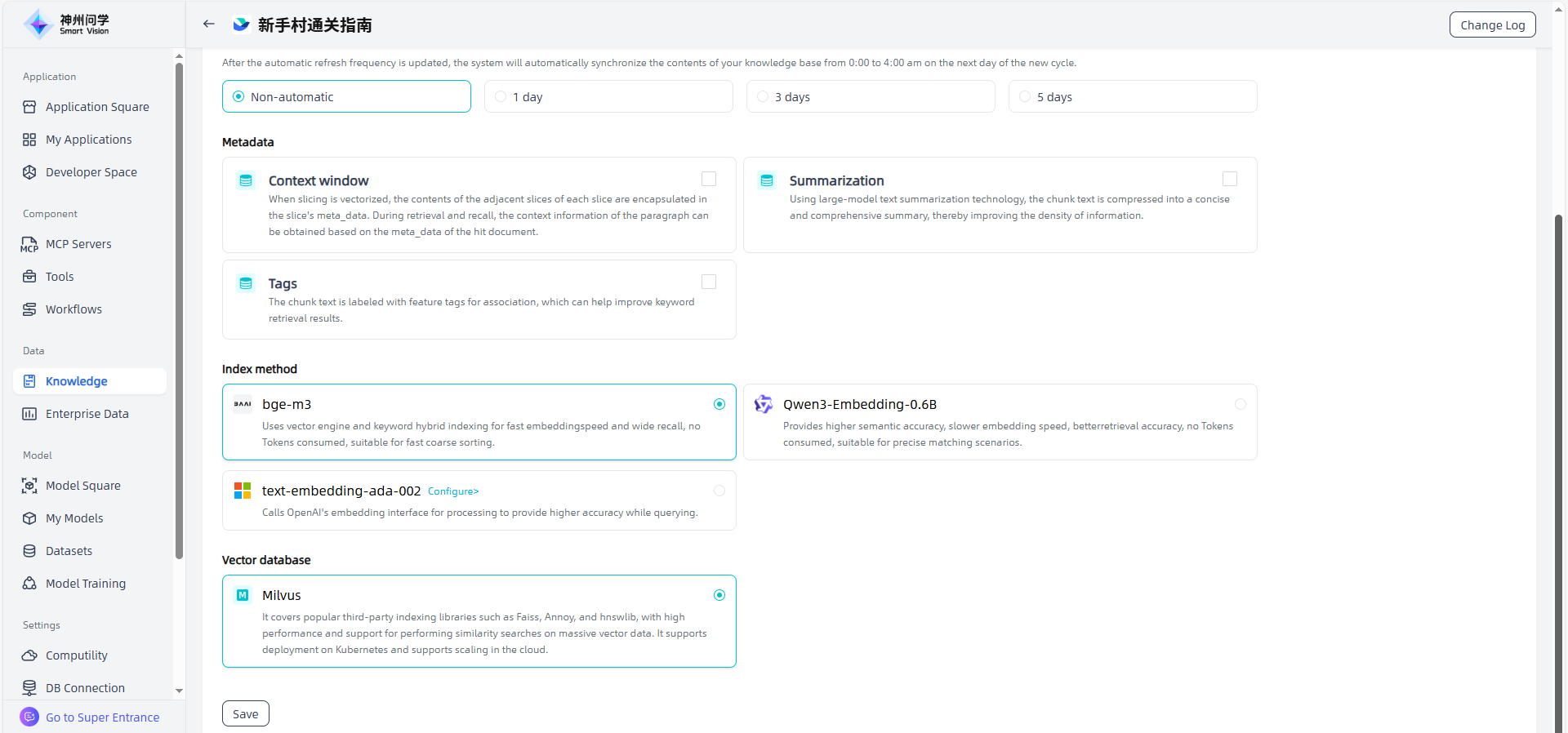
Metadata Extraction:Optional, you can select it as needed.
- Context window: When slicing is vectorized, the contents of the adjacent slices of each slice are encapsulated in the slice's meta_data. During retrieval and recall, the context information of the paragraph can be obtained based on the meta_data of the hit document.
- Summarization: Using large-model text summarization technology, the chunk text is compressed into a concise and comprehensive summary, thereby improving the density of information.
- Tags: The chunk text is labeled with feature tags for association, which can help improve keyword retrieval results.
Index Configuration:
- Index mode: The embedding process is to encode unstructured data into vectors, converting the knowledge and information of the enterprise into a vector form that can be understood by computers, just like encoding the contents of a book into library index cards so that the information can be quickly retrieved.
- bge-m3: Hybrid vector-keyword indexing; fast embedding, wide recall, no Token consumption; suitable for rough search.
- Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B: Supports higher semantic precision, slower embedding, no Token consumption; suitable for precise matching.
- text-embedding-ada-002: Uses Azure OpenAI embedding API for more accurate query results.
- Vector database: Its main function is to store and process vector data and provide efficient vector retrieval functions.
- Milvus: It covers mainstream third-party index libraries such as Faiss, Annoy, and hnswlib. It has high performance, supports similarity search for massive vector data, supports Kubernetes deployment, and supports expansion on the cloud. For example, if you need a vector database that is easy to expand, stable and efficient, and supports multiple indexing methods, Milvus may be a better choice.
- Oracle: Use Oracle AI Vector Search for vector storage and efficient semantic similarity retrieval of any data, without the need for a dedicated vector database, supporting Oracle 23ai and above versions.
- Index mode: The embedding process is to encode unstructured data into vectors, converting the knowledge and information of the enterprise into a vector form that can be understood by computers, just like encoding the contents of a book into library index cards so that the information can be quickly retrieved.
Operation Guide
Start: In "Data - Knowledge", click the "Create Knowledge" button in the upper left corner to enter the "Create Enterprise Knowledge Base" page.
Fill in the enterprise knowledge base information: including the knowledge base name and description, click the "OK" button to start creating the enterprise knowledge base.
Add governed file: After filling in the enterprise knowledge base information, enter the knowledge base details page, click "Add Governance File" to add files and carry out knowledge governance. (Note: Adding files through the "Add Files" portal only allows for text Chunk and cleaning, and cannot handle knowledge management)
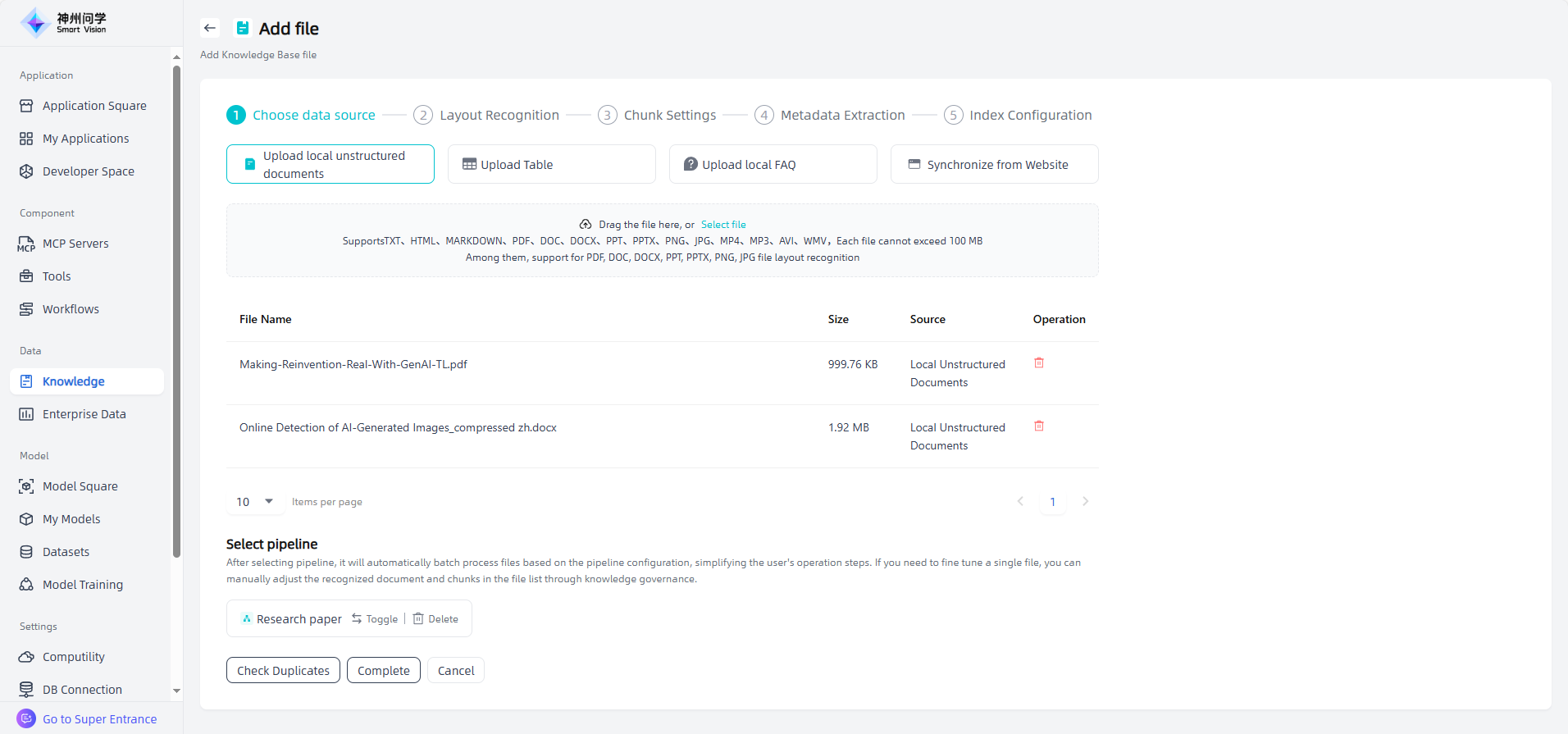
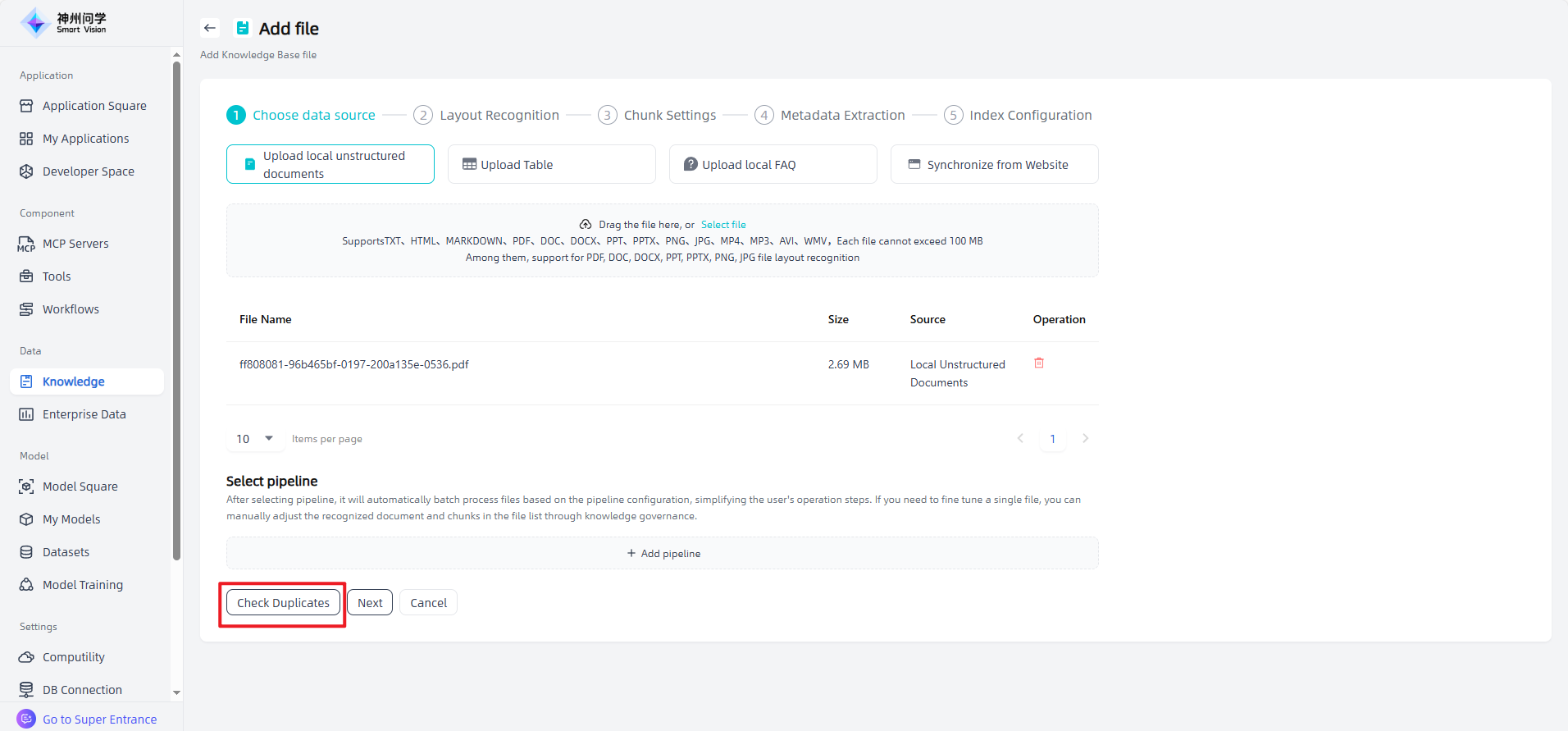
The enterprise knowledge base supports adding four types of files: local unstructured documents, local tables, local FAQ, and synchronize from Website.
Upload local unstructured documents: Upload knowledge base files that meets the required format and size by dragging and dropping the file or selecting the file.
Upload Table: Upload knowledge base files that meets the required format and size by dragging and dropping the file or selecting the file.
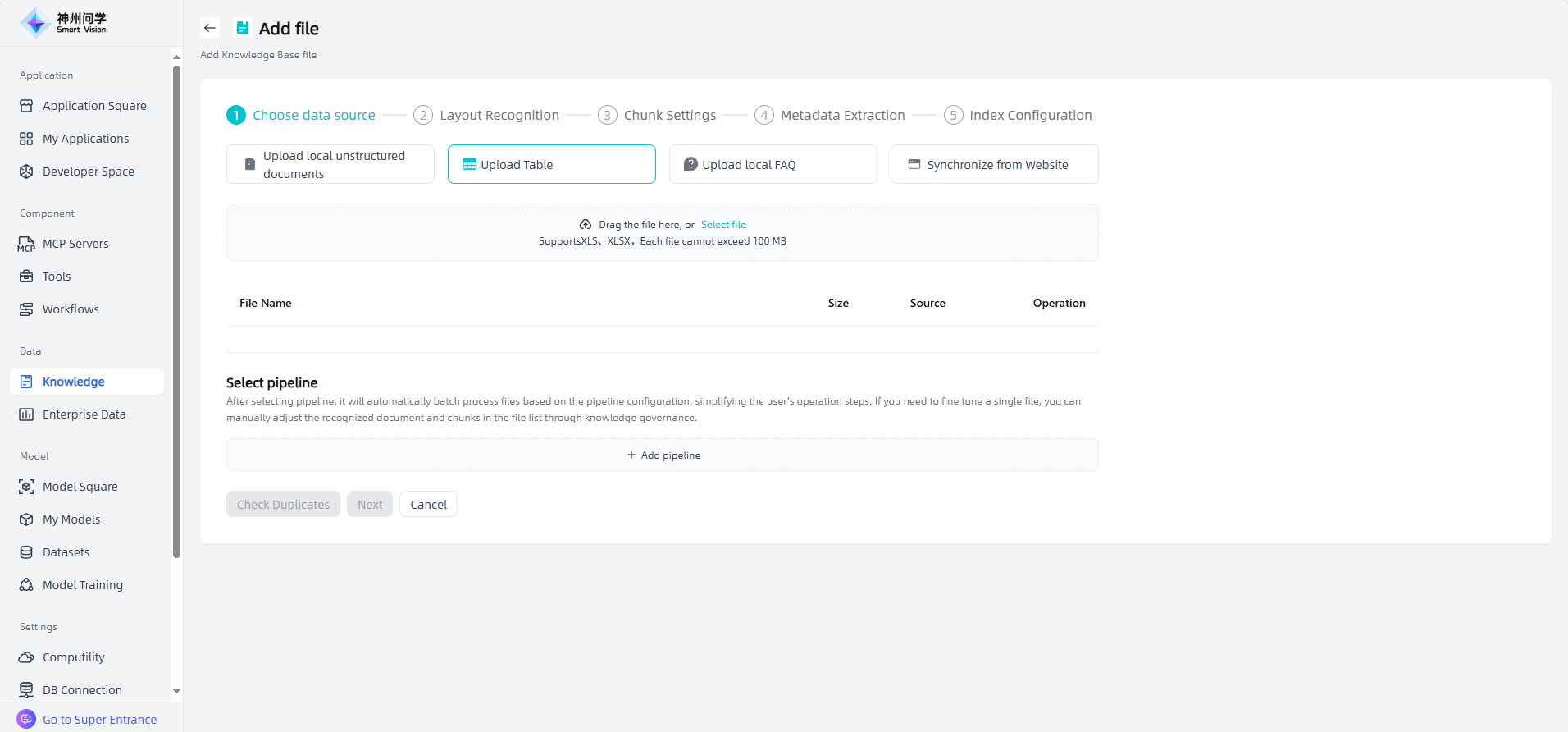
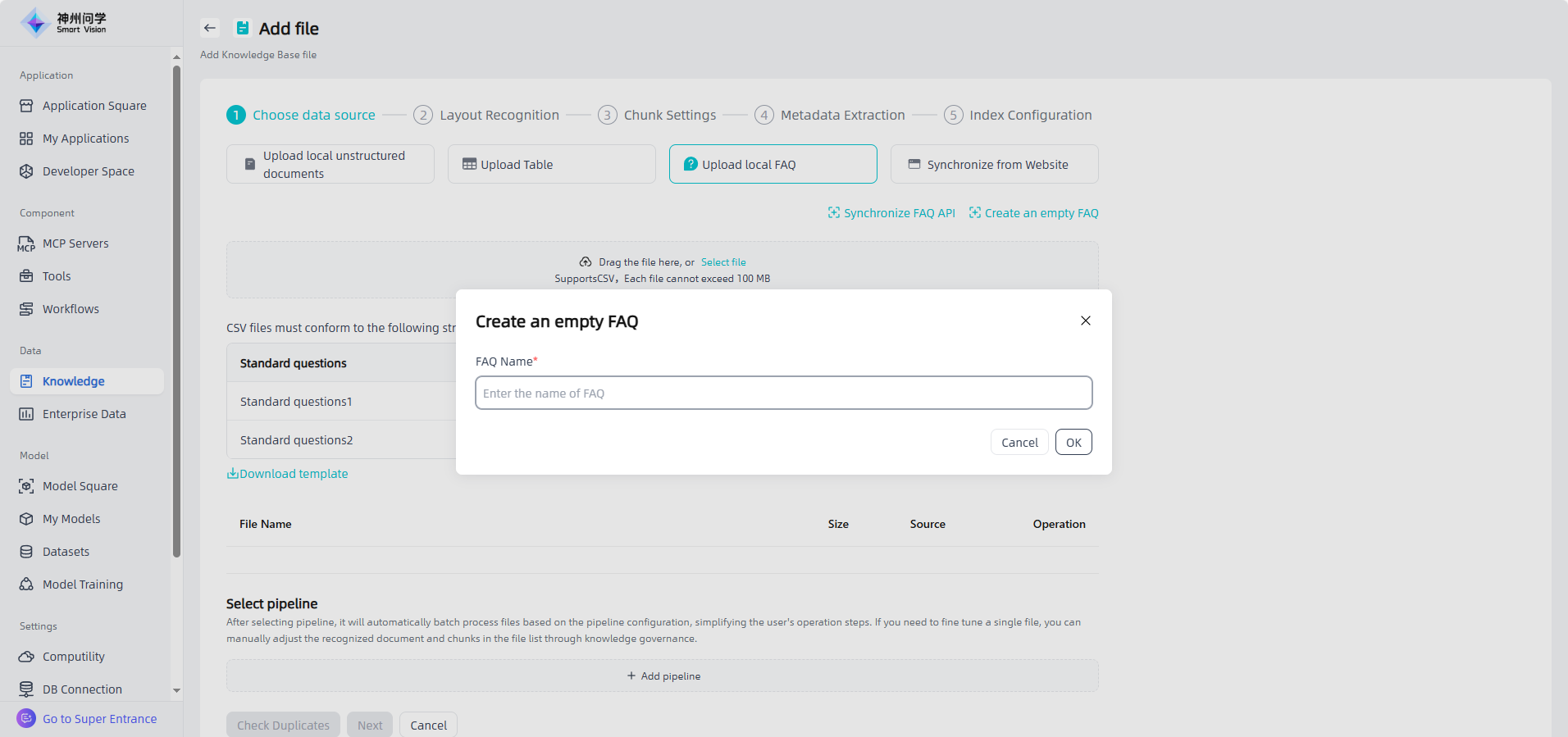
Upload local FAQ: Upload knowledge base files that meets the required format and size by dragging and dropping the file or selecting the file. You can download the template, edit it according to the template and then upload it. You can also click "Synchronize FAQ API" to import it through API synchronization. You can also directly click "Create an empty FAQ", so that you can add chunk information directly to the empty FAQ later.
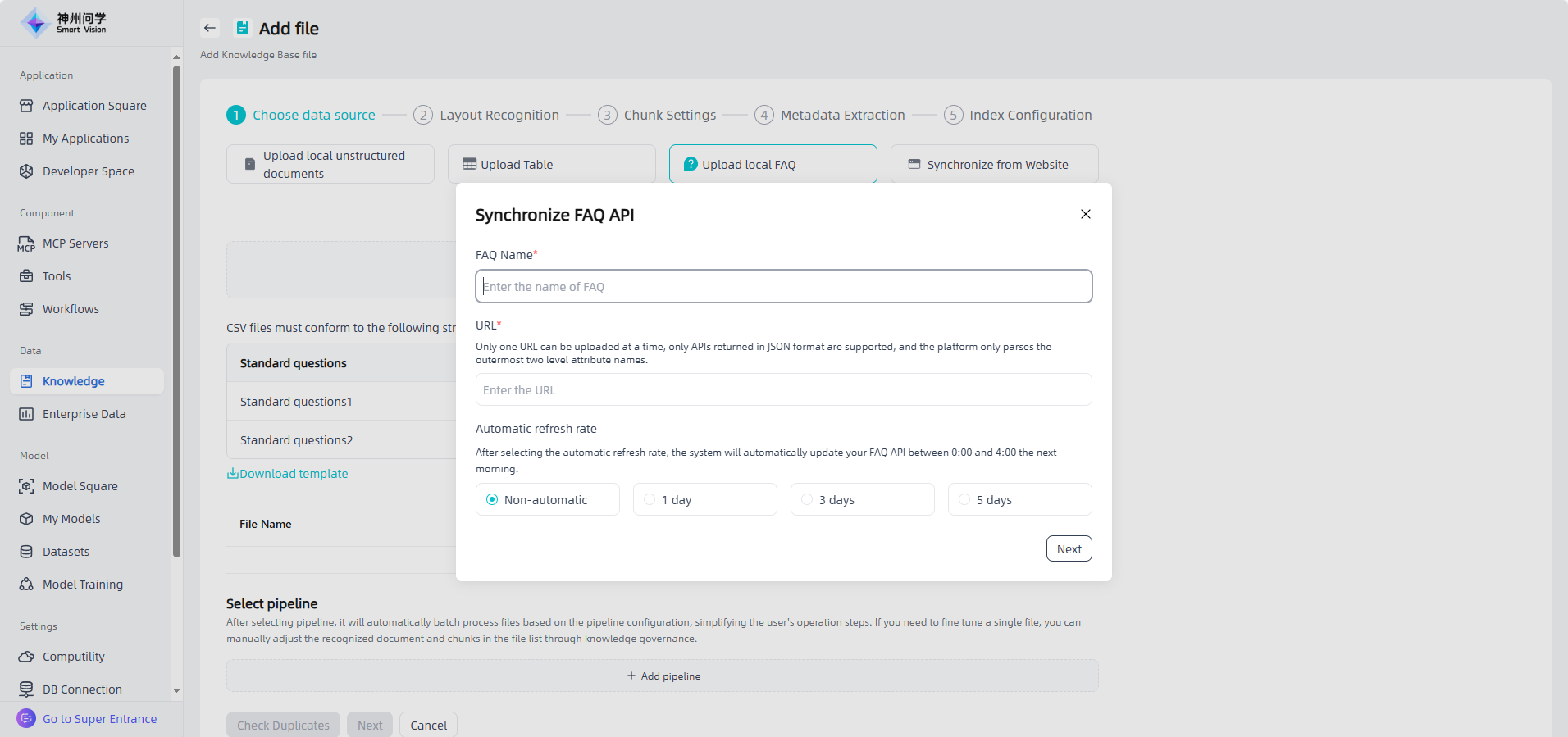
Synchronize from Website: You need to fill in the web link, set the automatic refresh frequency, and extract data to complete this type of file addition.
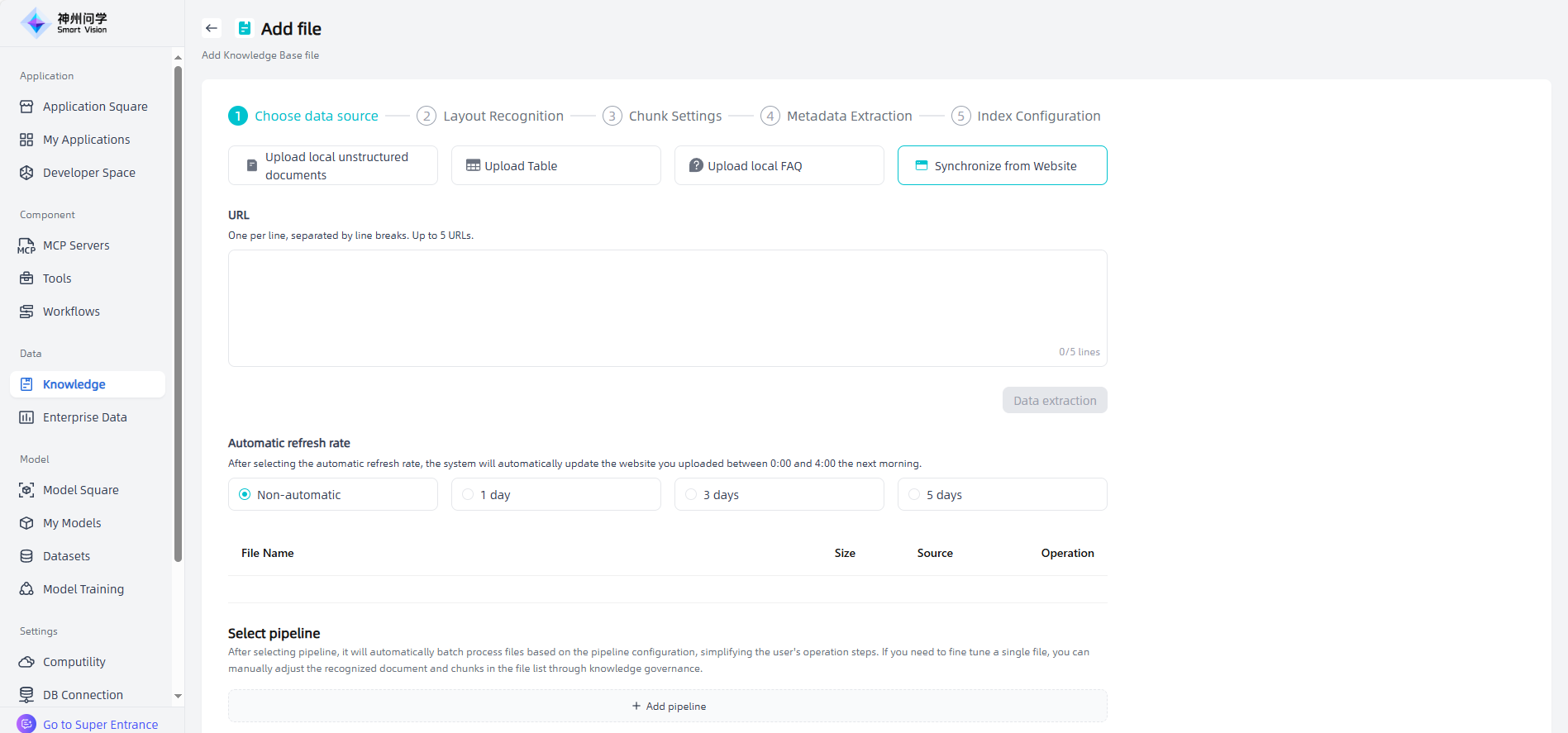
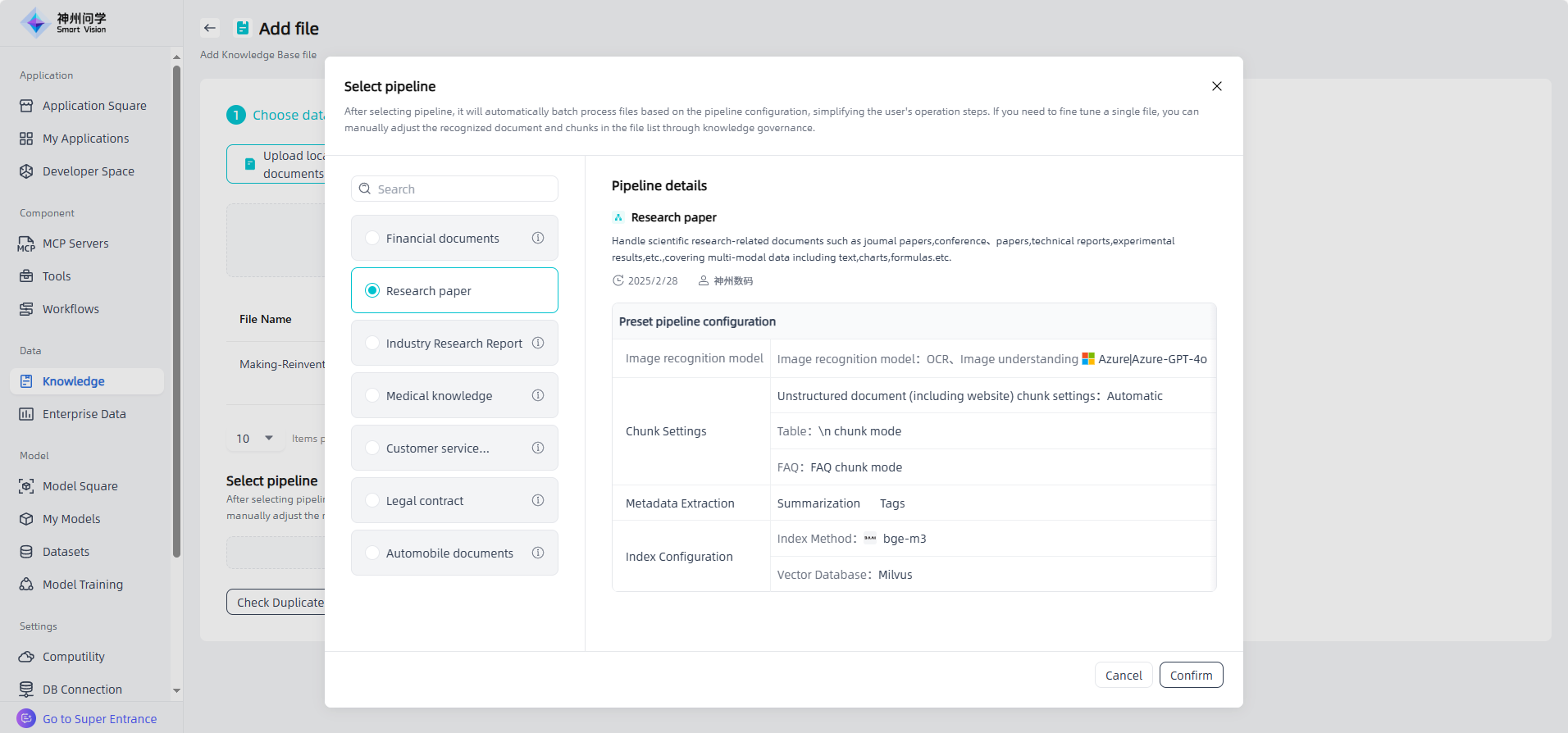
Knowledge governance: The added files will be displayed in the "Add Files" list. You can choose: ① Click "Next" to gradually complete the knowledge governance related settings; ② Click on "Add pipeline" and select the knowledge governance template to achieve automated batch processing.
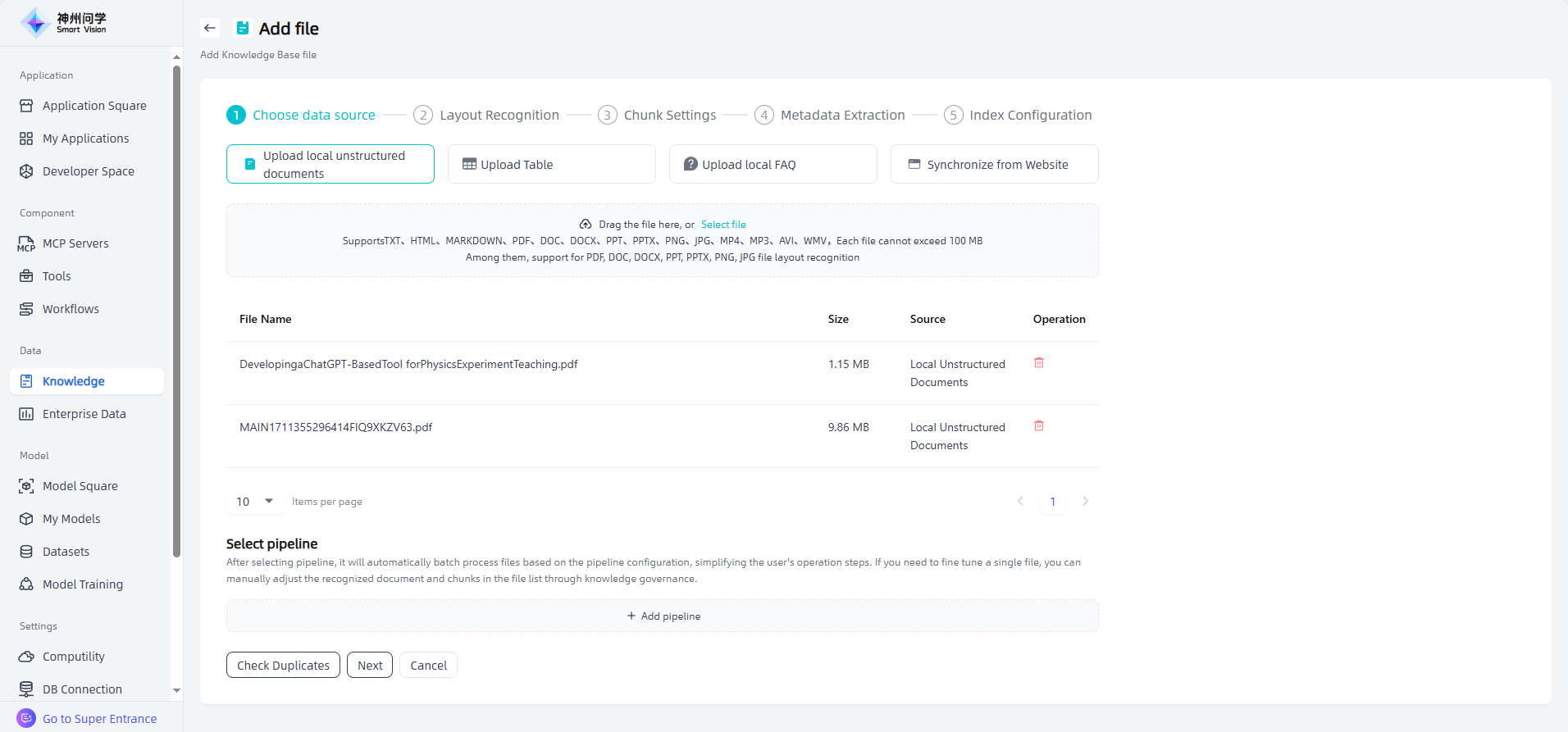
Gradually set knowledge governance
①Layout Recognition: After adding the file, click "Next" to enter the layout recognition page. The left side of the page displays the original documents uploaded by the user (PDF, DOC, DOCX, PPT, PPTX, PNG, JPG), and the right side displays various layout elements recognized through models/tools (titles, text, images, tables, formulas, etc., which are formatted and converted into multimodal Markdown format). When users add files in bulk, only the recognized documents are previewed and loaded. Users can switch files to view the layout of different files and recognize the original and recognized documents. If there are no PDF, DOC, DOCX, PPT, PPTX, PNG, JPG files in the files uploaded by the user at a time, the layout recognition step will be skipped and the chunk settings will be entered directly. Users can switch and select the appropriate layout recognition model as needed.
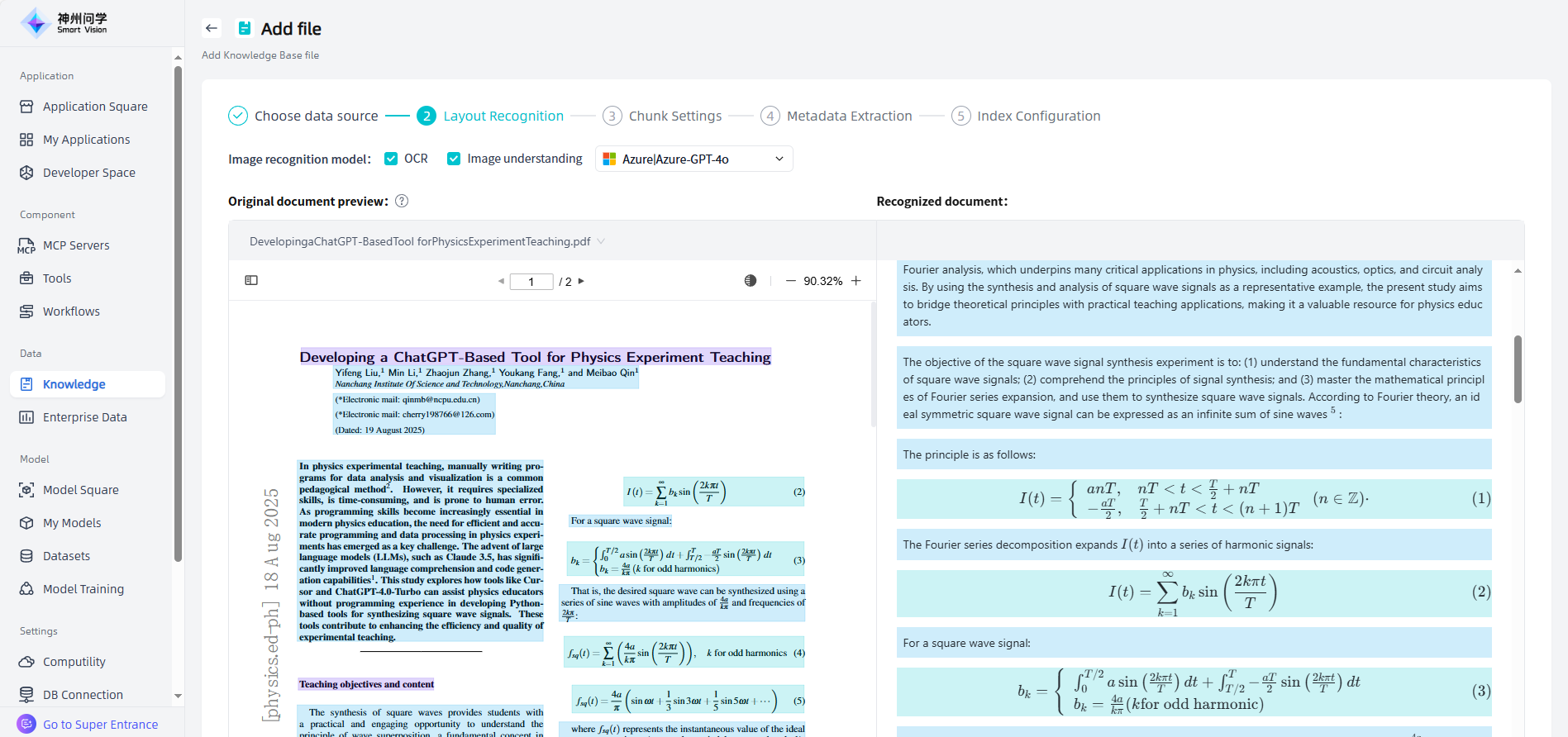
②Chunk Settings: After layout recognition, click "Next" to enter the chunk settings page. The left side of the page displays the chunk settings rules for different types of documents (unstructured document, table, FAQ). Users can choose the appropriate splitter as needed and preview the MD file sliced in chunks in the right workspace.
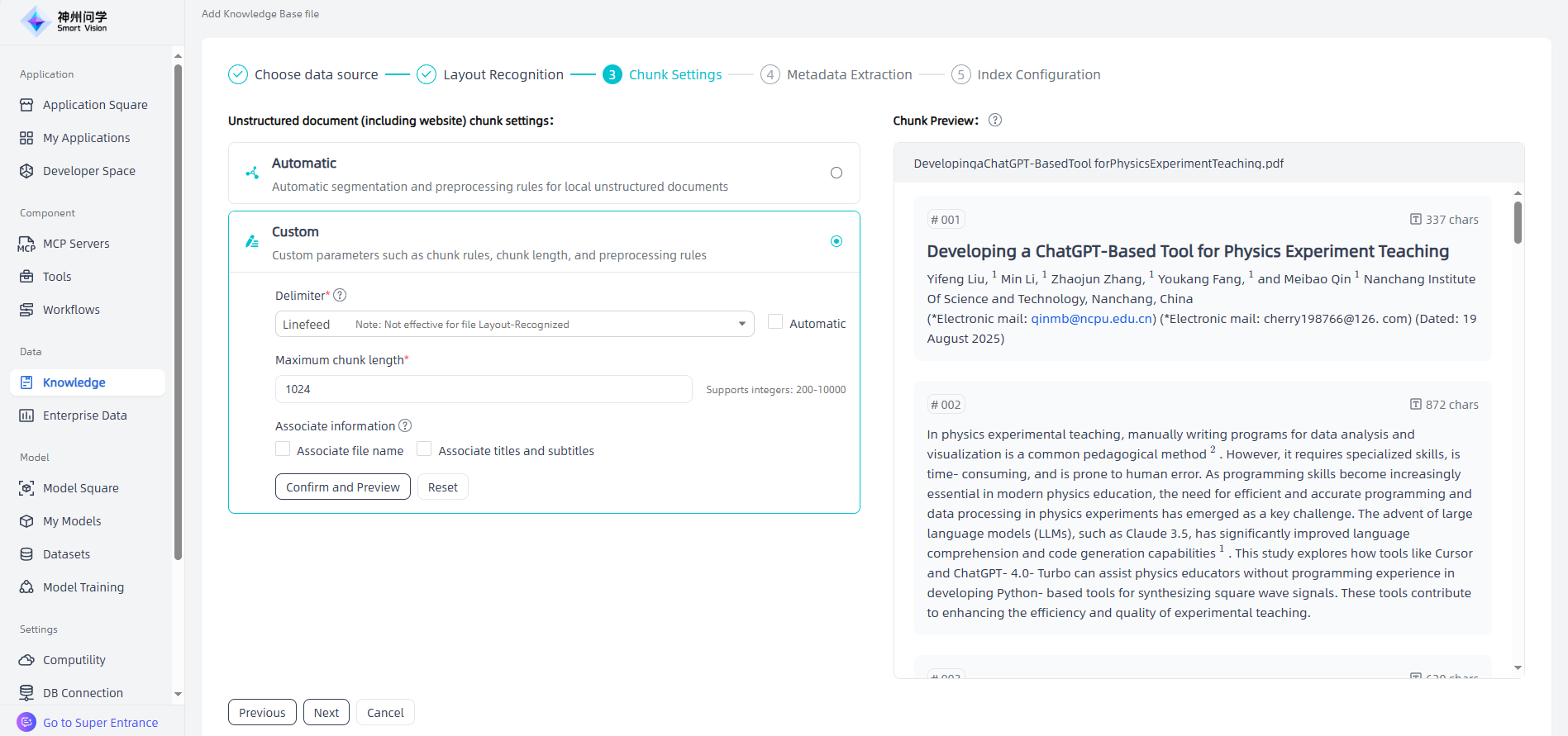
③Metadata Extraction: After chunk settings, click "Next" to enter the metadata extraction page. The left side of the page supports users to select metadata extraction information as needed, and the chunks and metadata preview are displayed on the right side.
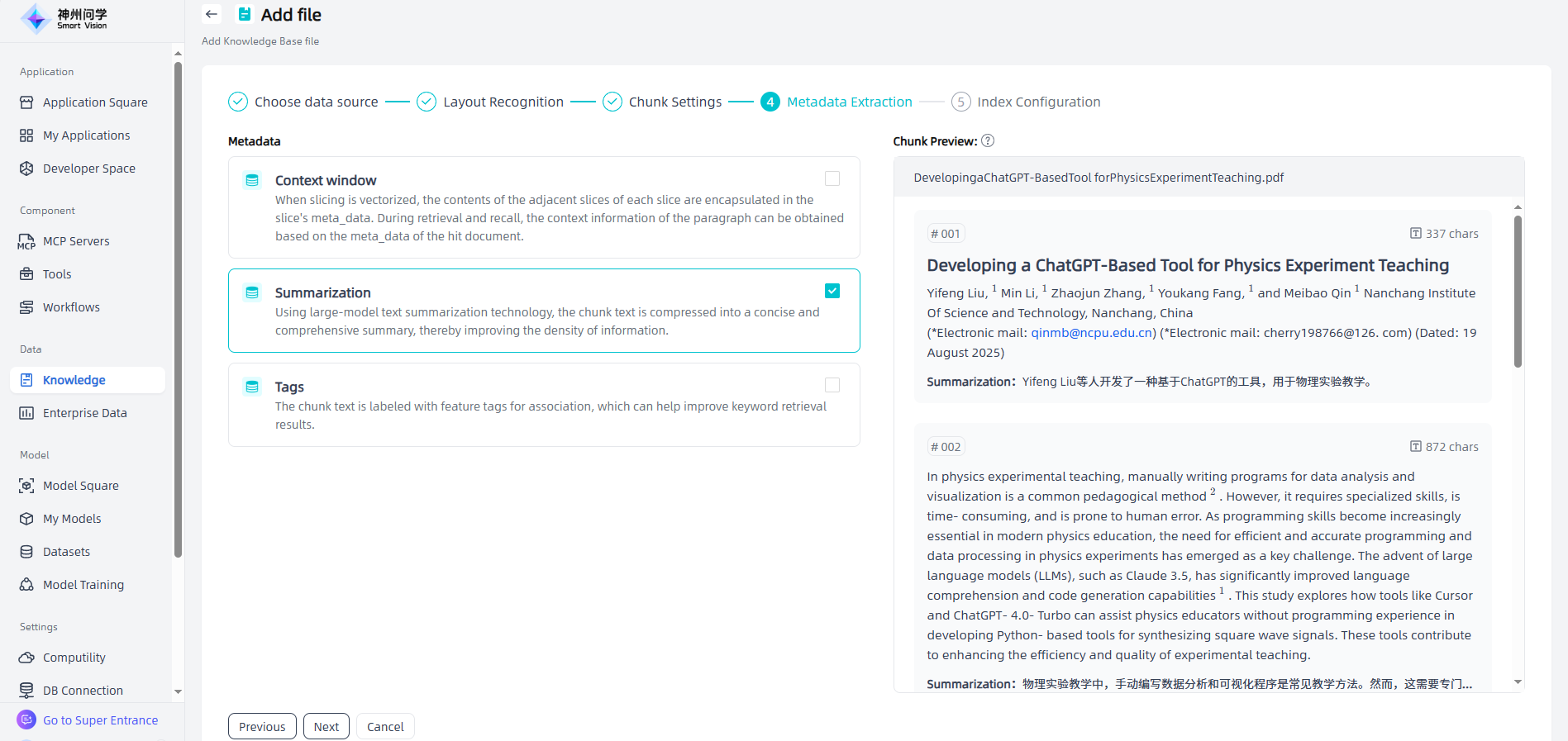
④Index Configuration: After extracting metadata, click "Next" to enter the index configuration page, where users can choose the index method and vector database as needed.
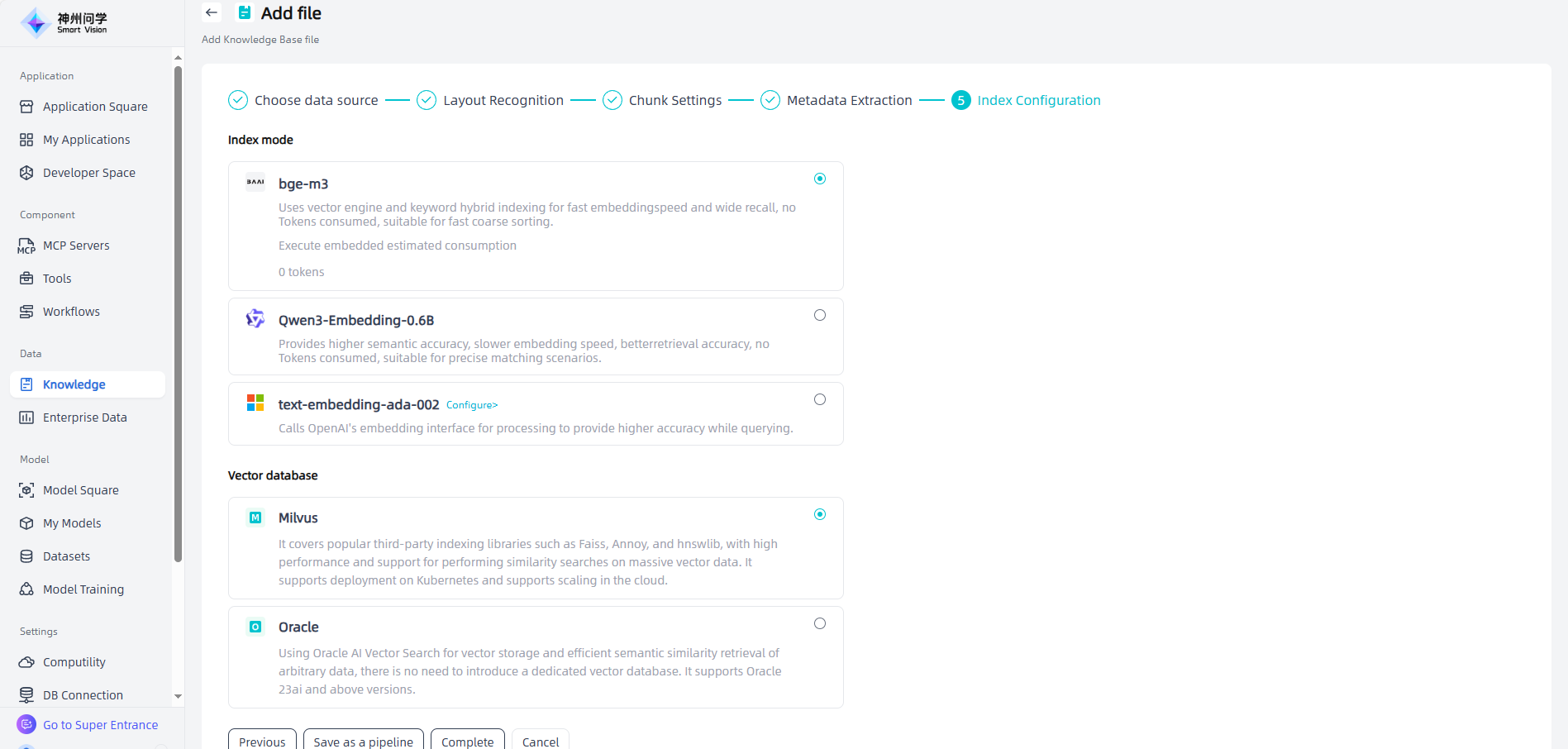
After completing the index configuration, click "Complete" directly, and the added files will appear in the knowledge base file list and begin embedding processing.
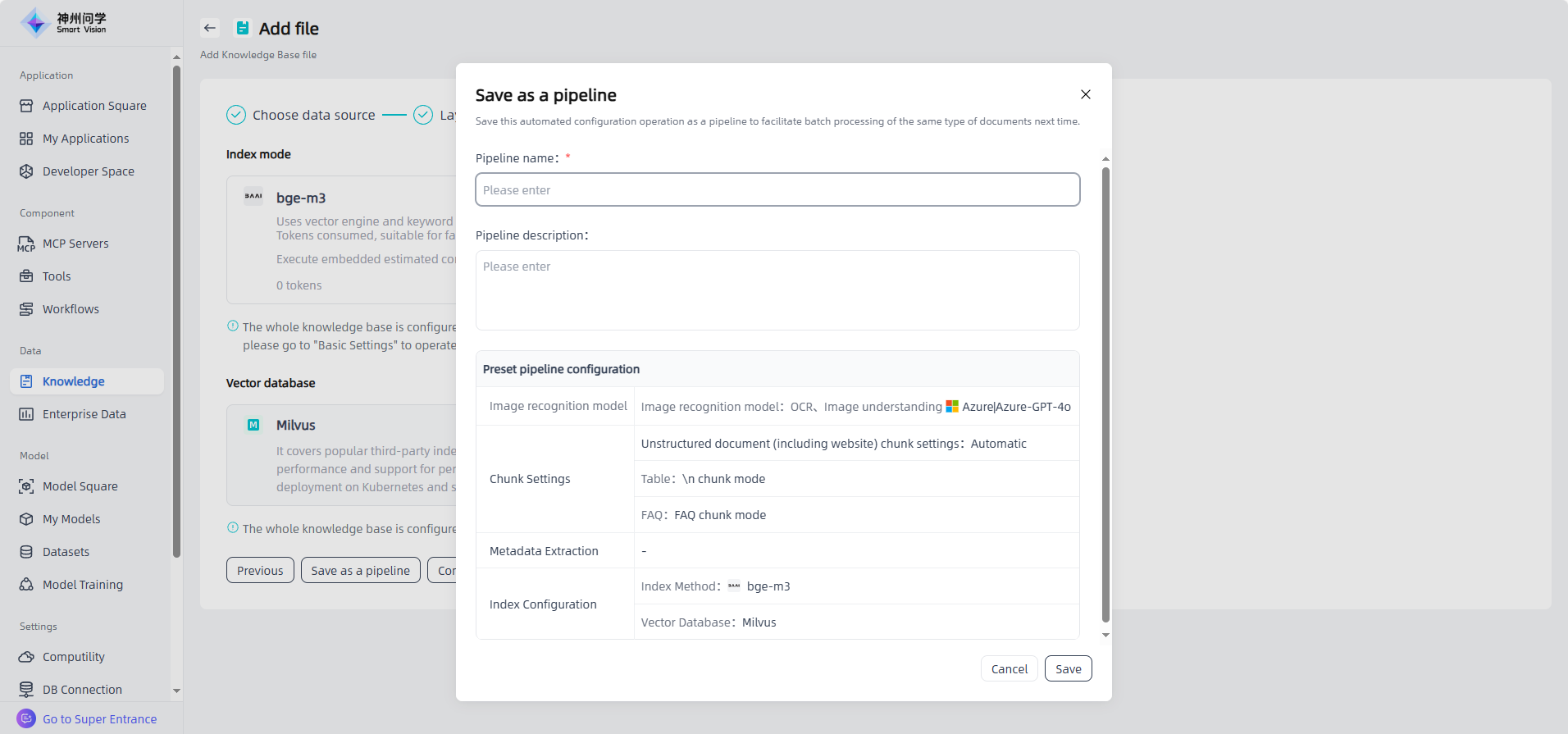
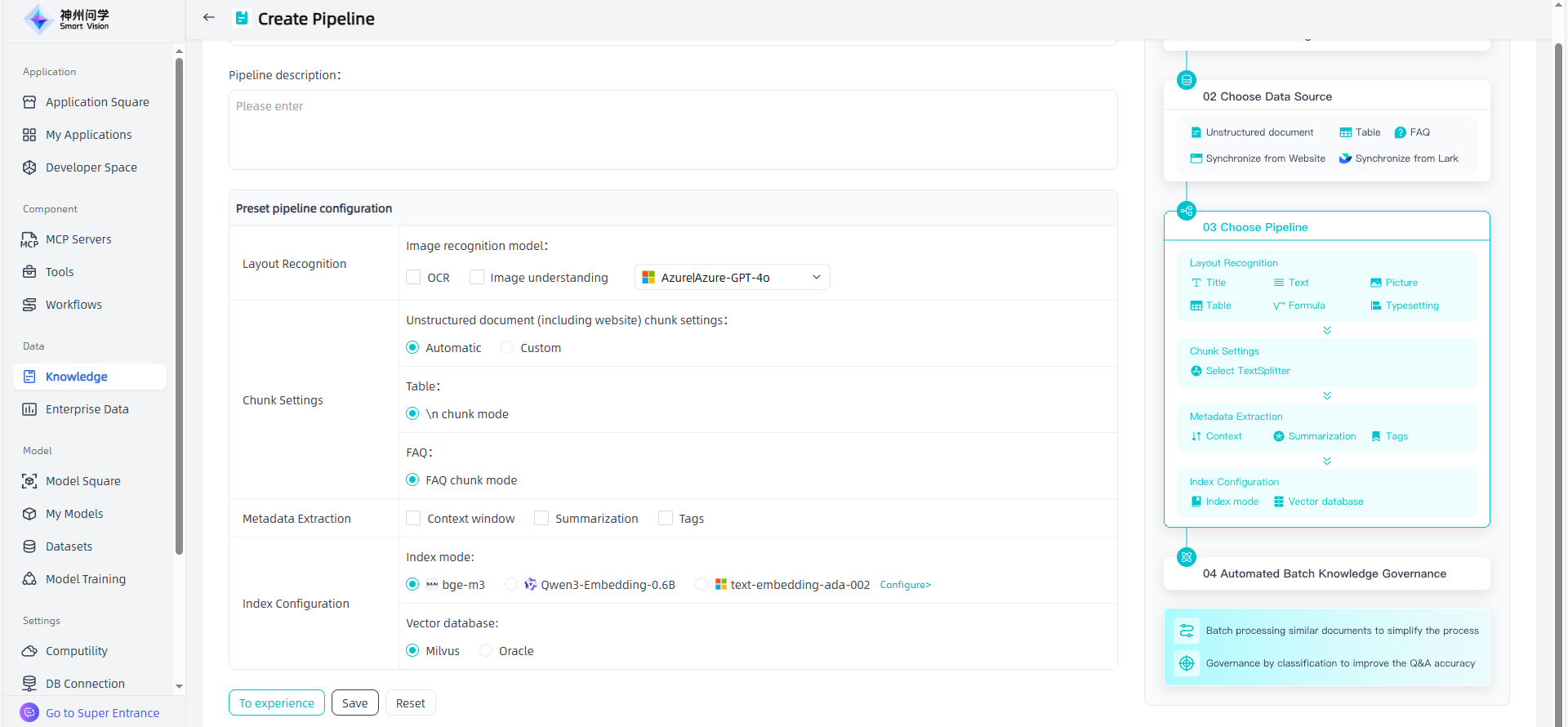
The relevant knowledge governance settings during this process support one click saving as a pipeline. Click the "Save as a pipeline" button to save this configuration operation and create a set of knowledge governance templates. After saving, they will be displayed synchronously in Knowledge - Pipeline.
Add pipeline
After adding files, click "Add pipeline", and users can select the appropriate pipeline (within the scope of Knowledge Pipeline and not conflicting with the basic settings of the knowledge base). After selecting the pipeline, click "Finish", and these files will appear in the list of knowledge base files and be automatically processed according to the pipeline.
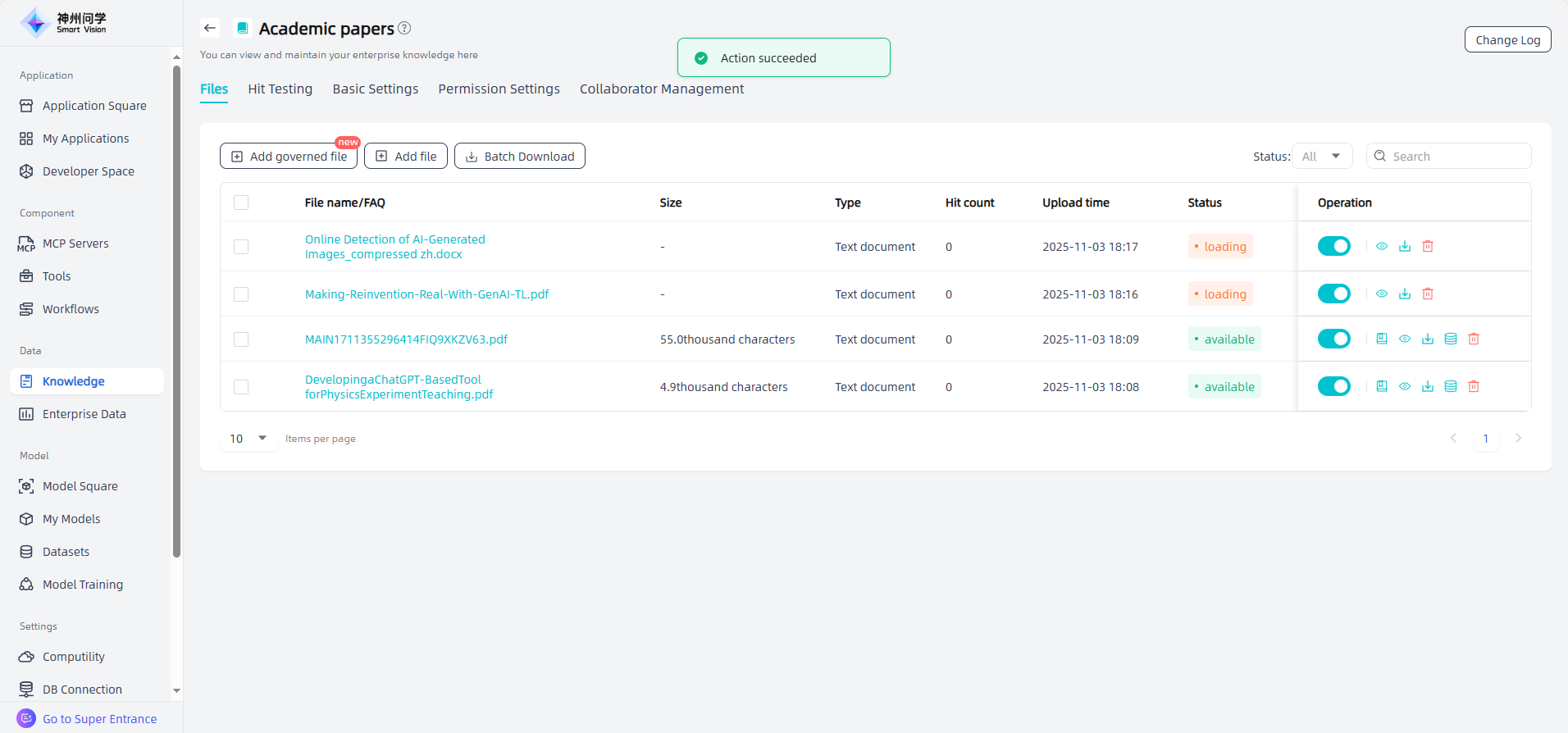
Manual governance: For files added through "Add Governance Files" in the knowledge base file list, unstructured documents other than tables and Q&A sets have a "Knowledge Governance" button. Clicking the "Knowledge Governance" button supports users to manually adjust the effect of layout recognition and chunk settings (PDF, DOC, DOCX, PPT, PPTX, PNG, JPG files). Knowledge governance includes layout recognition and chunk settings; TXT, HTML, MARKDOWN, MP4, MP3, AVI, WMV file knowledge governance can only adjust chunk settings.
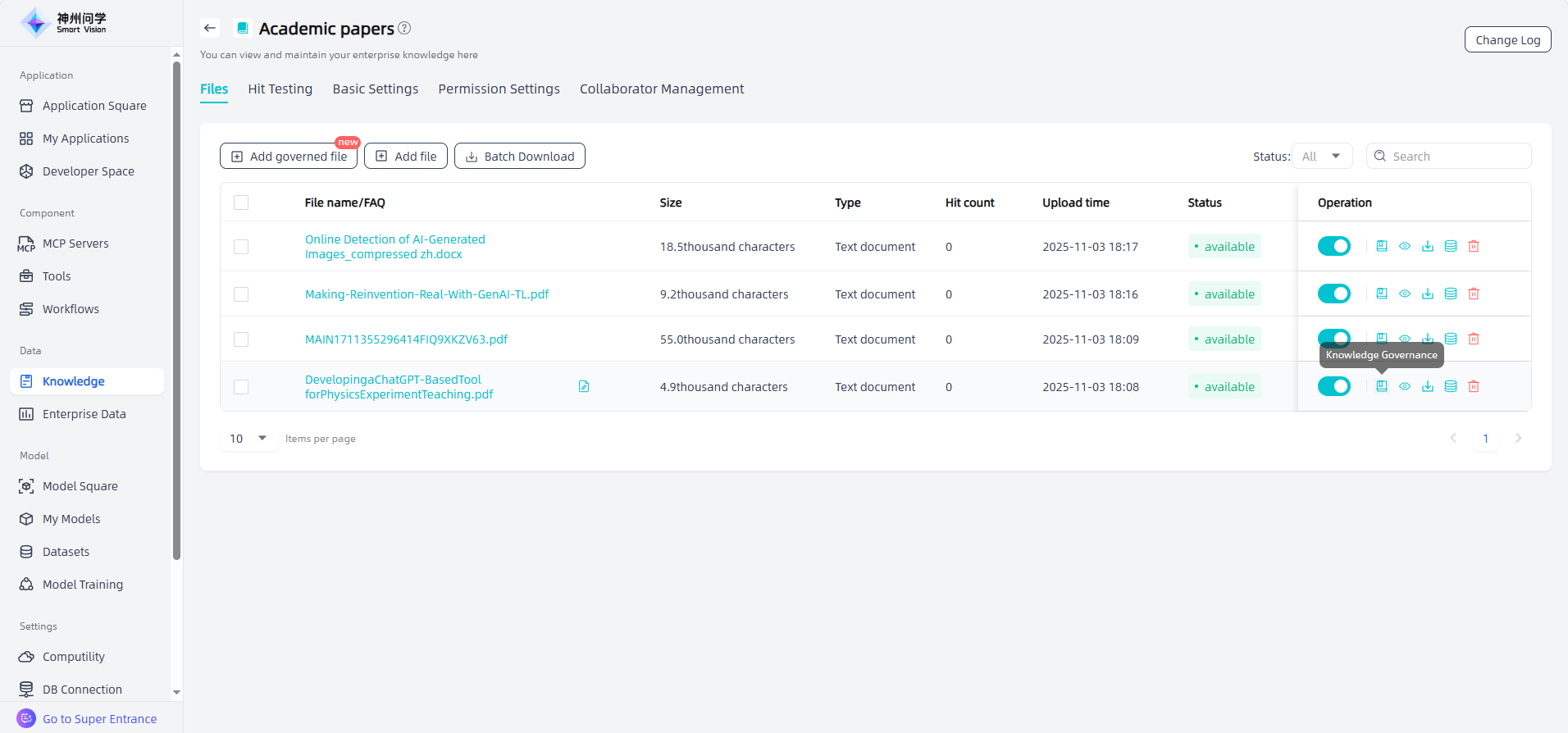
① Layout recognition: PDF, DOC, DOCX, PPT, PPTX, PNG, JPG files added through "Add Governance File" support manual adjustment of layout recognition results. Click the "Knowledge Governance" button to adjust the layout recognition results. The left workspace is the corresponding original file, and the right workspace is the recognized document. Users can adjust the order by selecting the parsed color blocks and dragging them, or click "Edit" to modify the content. After editing, clicking outside the box will save (if the system recognizes that the user has modified a lot of content, it will prompt). For images, tables, and formulas, the workspace on the right defaults to displaying their original styles. You can click "Display OCR results" to display the OCR text of all images/tables/formulas, or hover over a certain image/table/formula and click "OCR results" to display its OCR text, and support editing and modification.
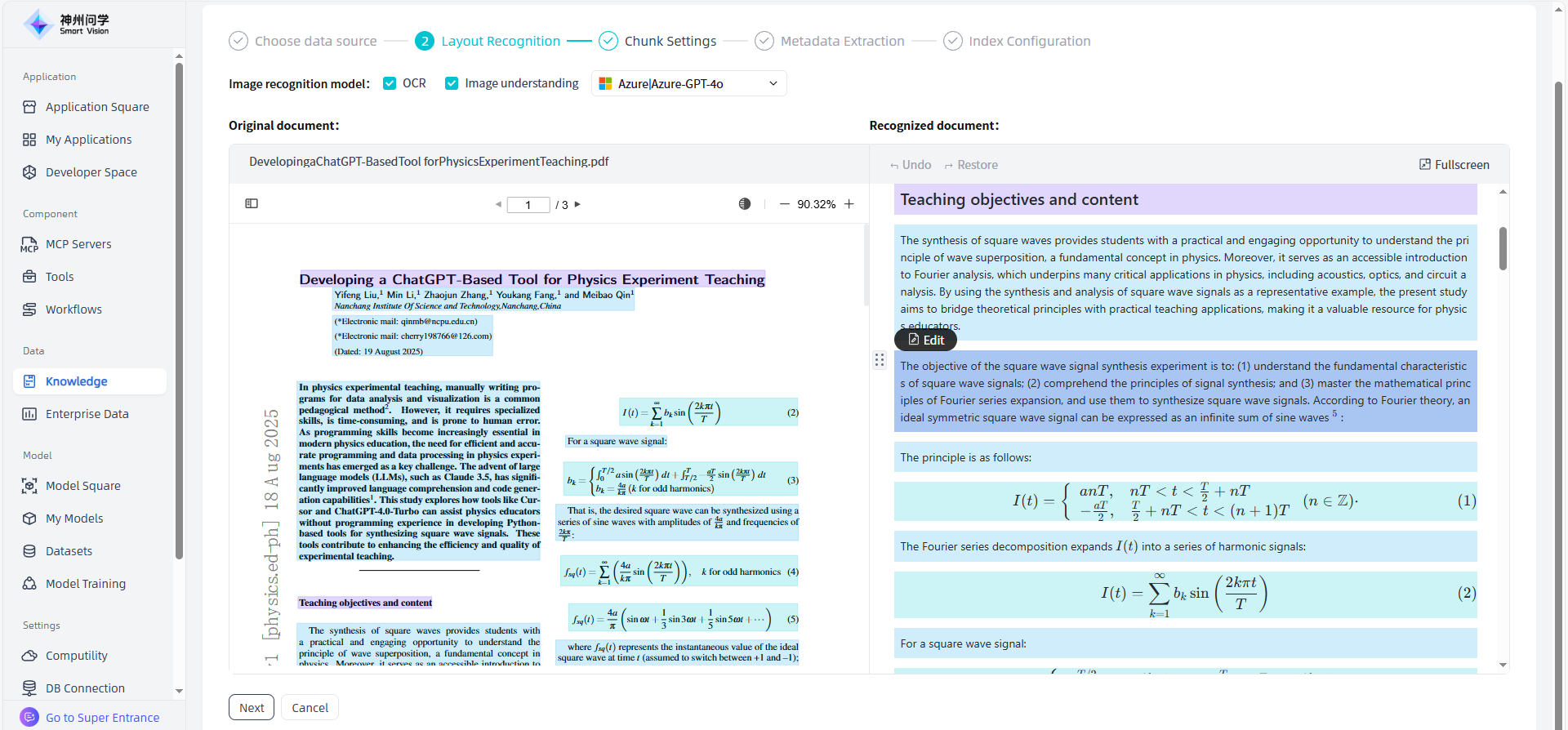
② Chunk settings: For PDF DOC、DOCX、PPT、PPTX、PNG and JPG files, click the "Knowledge Governance" button, you can manually adjust the chunk settings by clicking "Next" on the layout recognition interface. For TXT、HTML、MARKDOWN、MP4、MP3、AVI and WMV files, click the 'Knowledge Governance' button, you can directly enter the chunk settings. On the left side, only the chunk setting data of the corresponding document is displayed, and users can modify the chunk settings. On the right side, the workspace displays MD files sliced in the corresponding chunk method. After adjusting the chunk settings, click "Save and Process" to complete manual management.
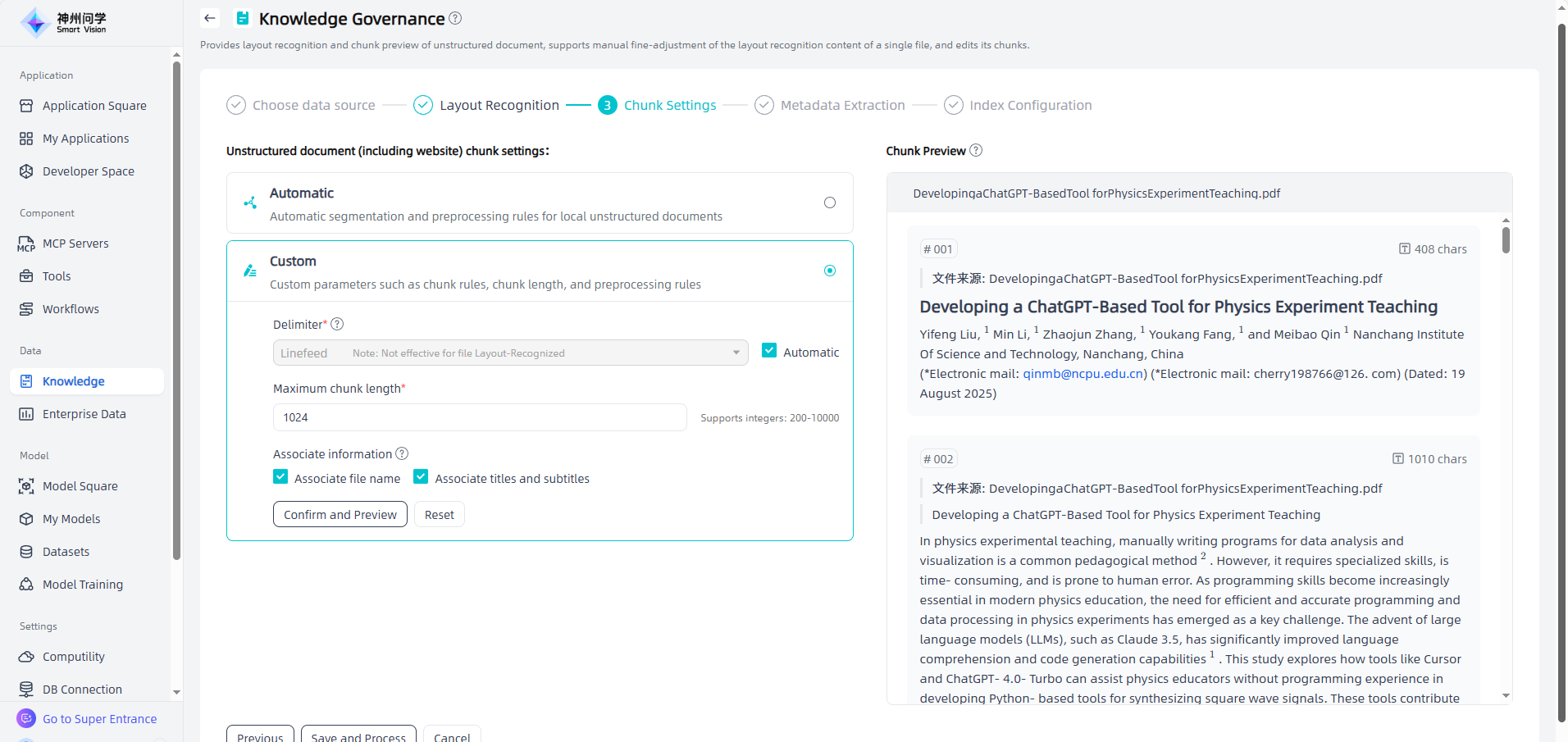
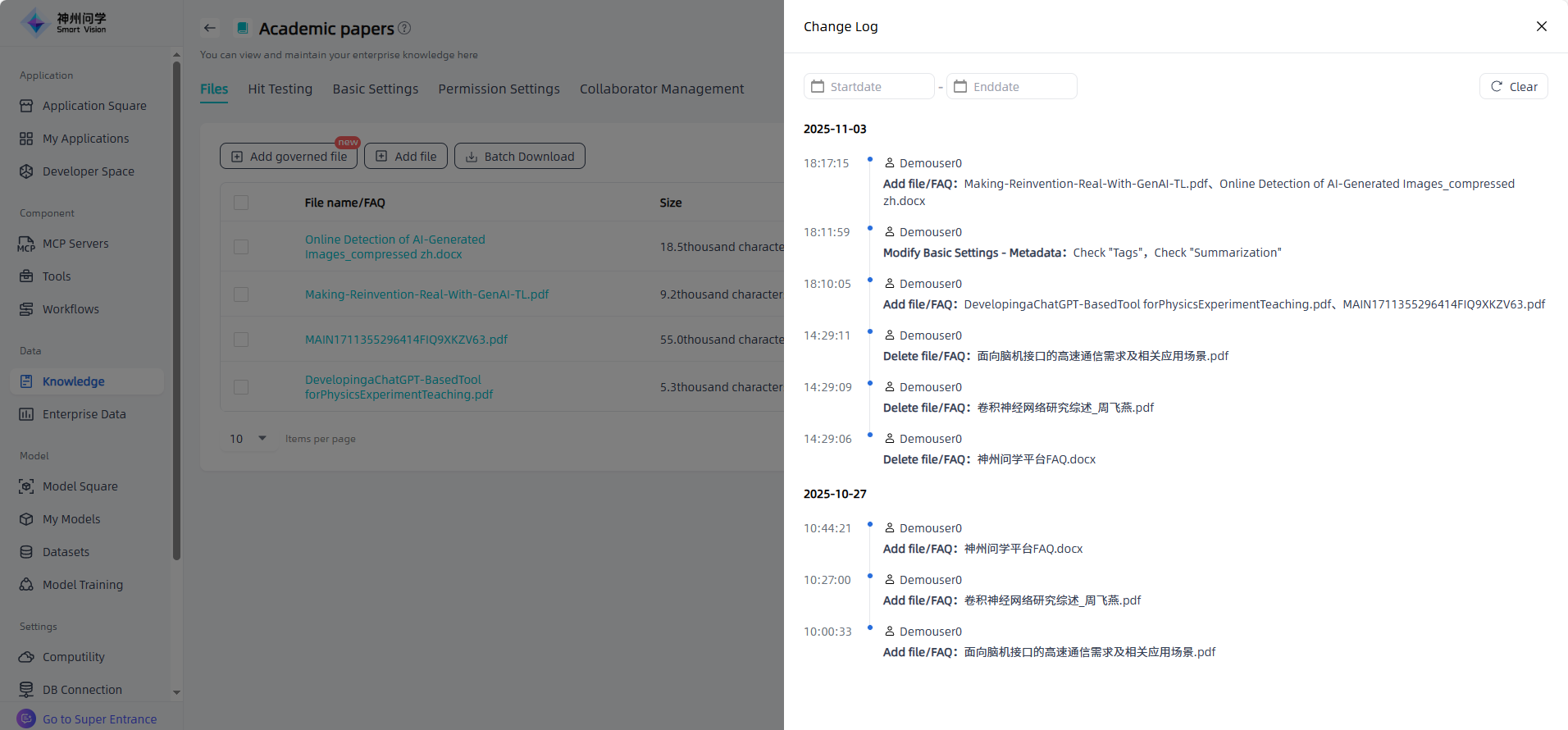
Edit and modify: You can modify, delete, set, and perform other operations on the knowledge base on knowledge base details, as well as view change records.
To add more files to the knowledge base, click on "Add governed file" on the knowledge base details page to perform the relevant operations. The enterprise knowledge base supports "Check Duplicates" . After uploading files, click the "Plagiarism check" button to compare the uploaded file with existing ones based on similarity, and you can customize the similarity threshold. To update a document, select "Smilarity Replace or not" to overwrite the previous version.
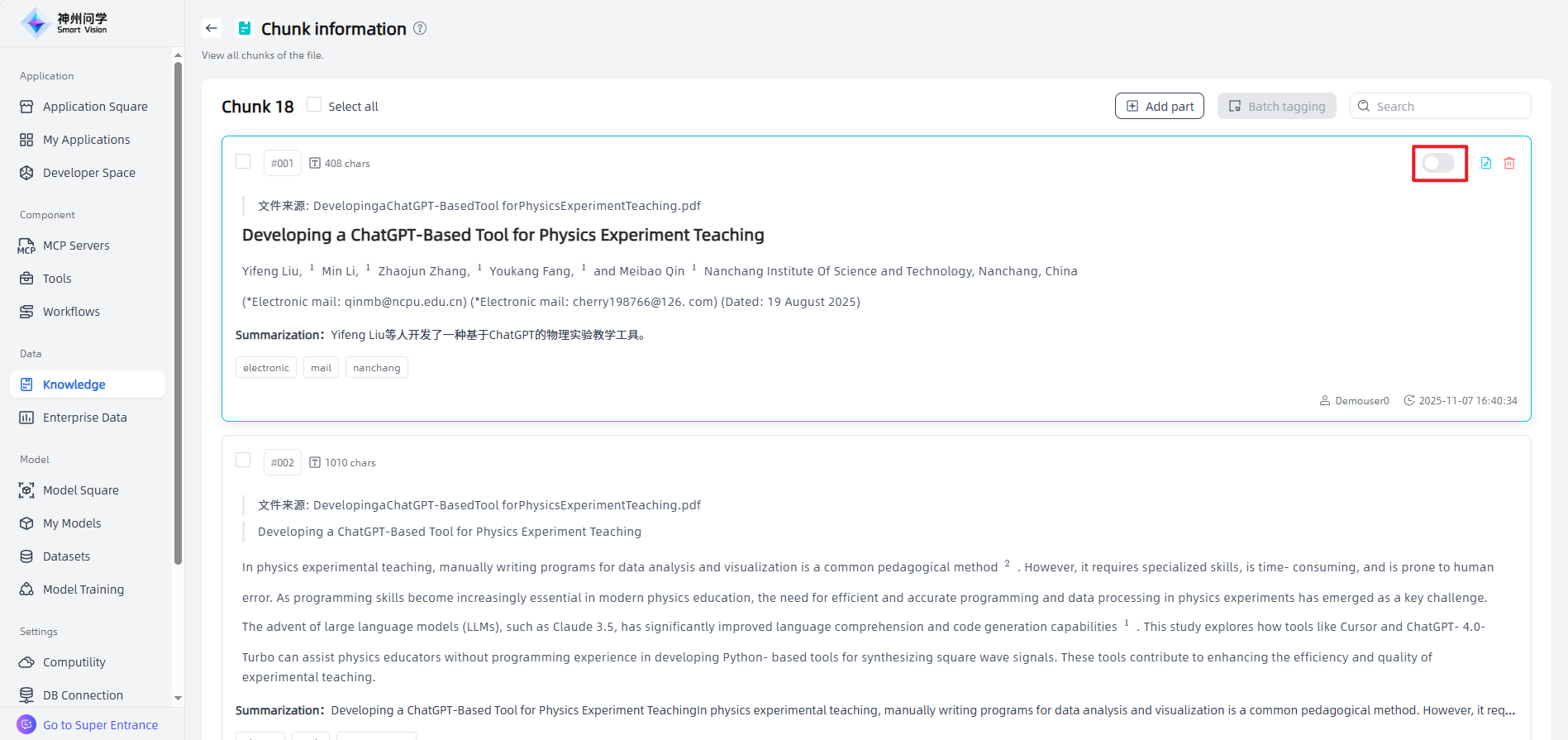
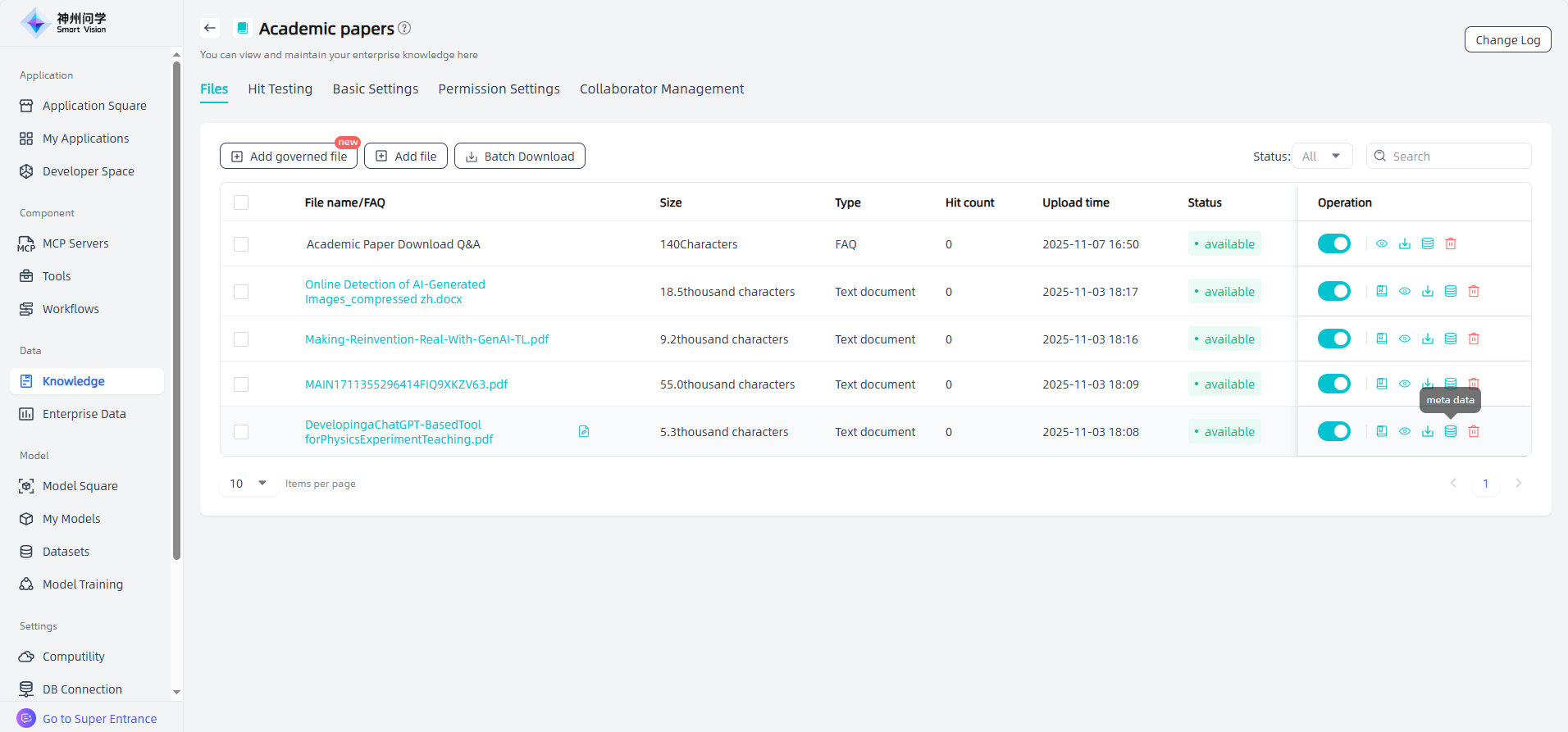
On the knowledge base details page, you can rename files, preview files, configure enable/disable settings, knowledge governance and text chunking/cleaning settings, view chunks, download files, maintain meta information, delete files, and perform other related operations.
View Chunks: For local unstructured documents, click the "View Chunks" button to view all chunks and adjust Chunk.

Users can edit an individual chunk by clicking the "Edit" button to open the chunk details page. In the "Chunk Details" window, you can freely switch between Rich text and Markdown editing modes. After editing, click "Save" to apply changes. You can also cancel or delete specific chunks using the corresponding buttons on the right side.

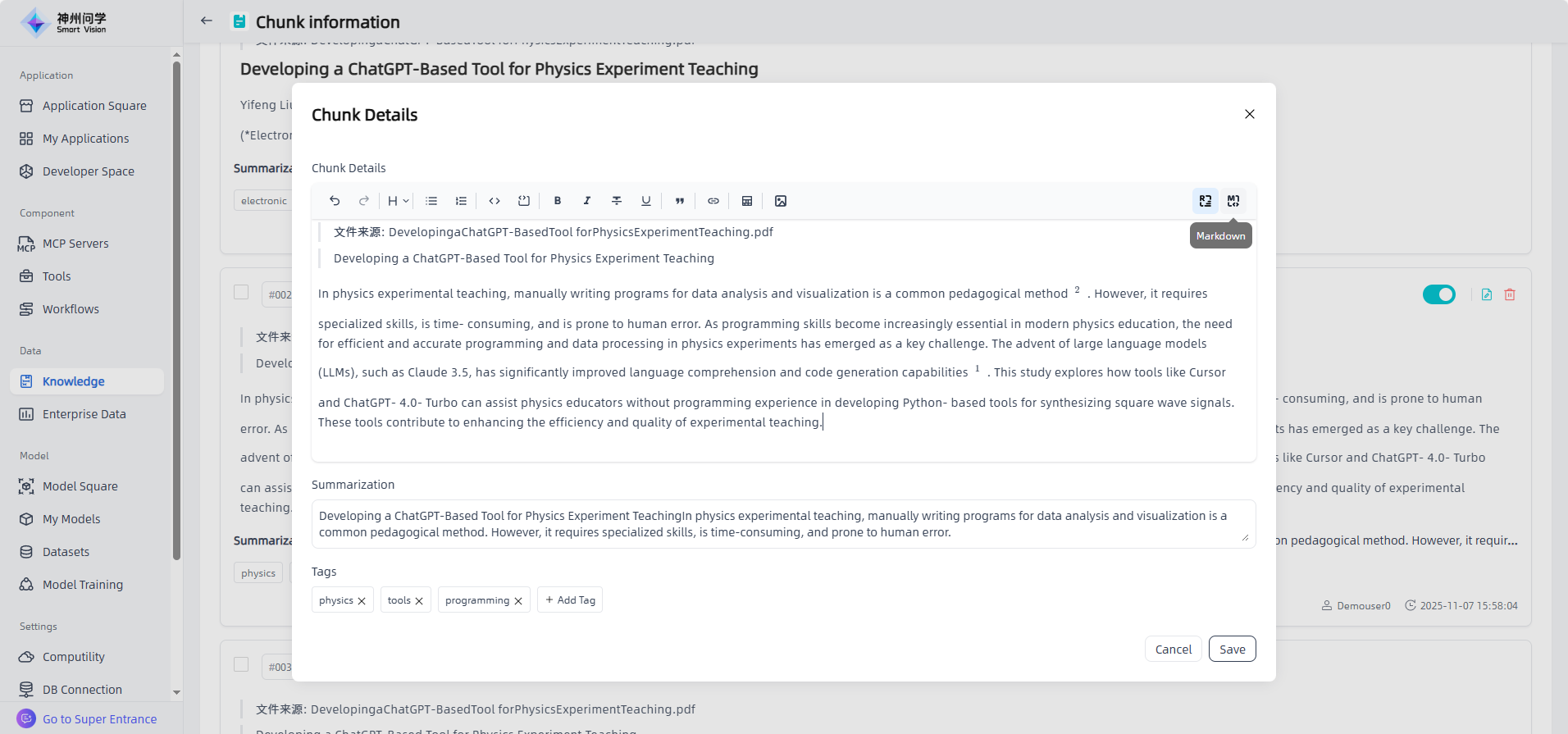
On the chunk information page, click "Add part" in the upper-right corner to create and edit a new chunk, then click "Confirm" to complete the addition.

For FAQ files (including empty FAQs), click the "View chunkts" icon to enter the Chunk information page, click "Add chunk" to add chunks . Each Answer can correspond to zero or multiple Questions, and rich text such as images and videos can be added within the Answer. For existing chunks, you can edit, enable or disable, move, or delete them.


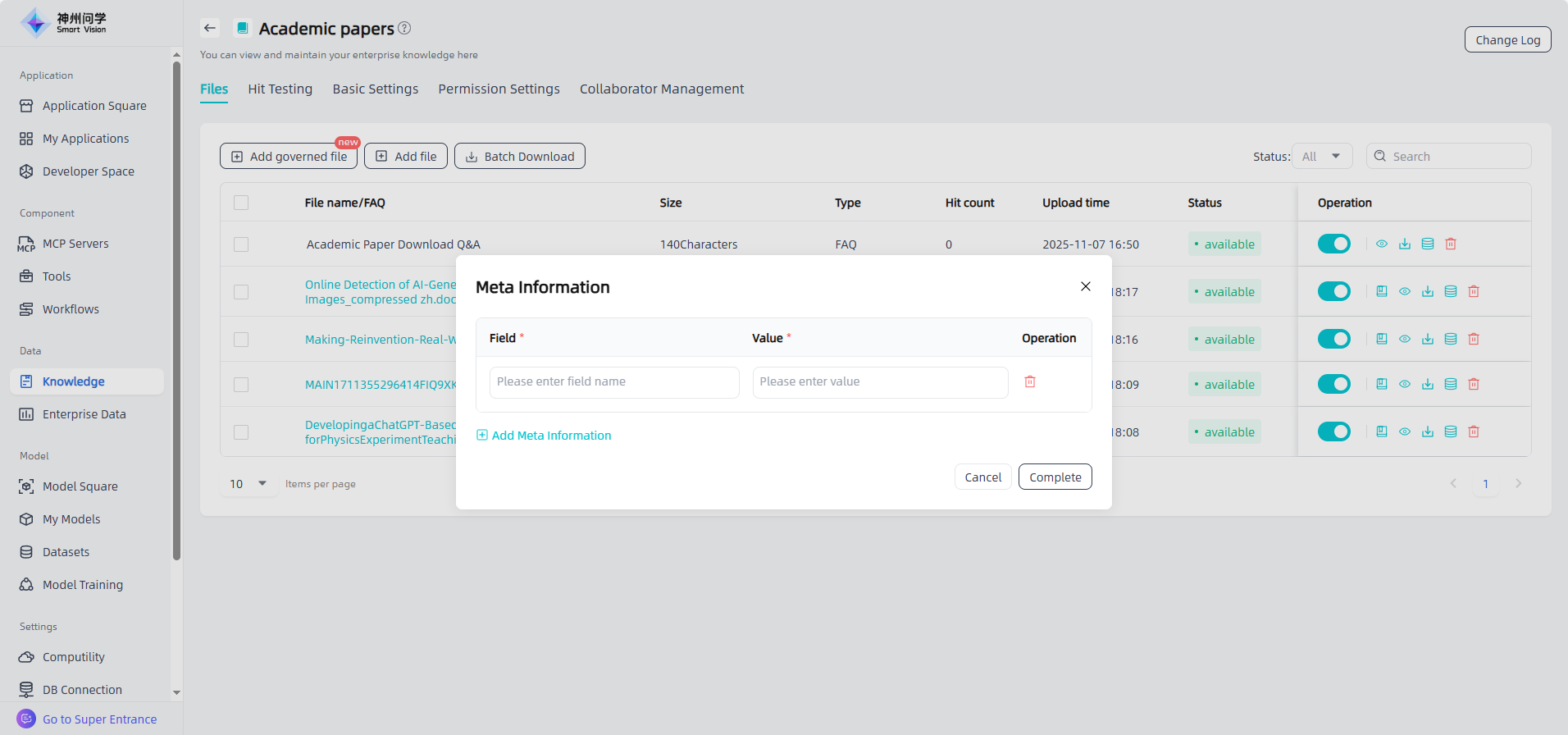
Meta Information: The knowledge base supports adding meta information to files. Meta information refers to a series of additional attributes related to the document content, integrated into text chunks in the form of key-value pairs. These attributes provide important contextual information and can significantly improve the accuracy of knowledge base retrieval.
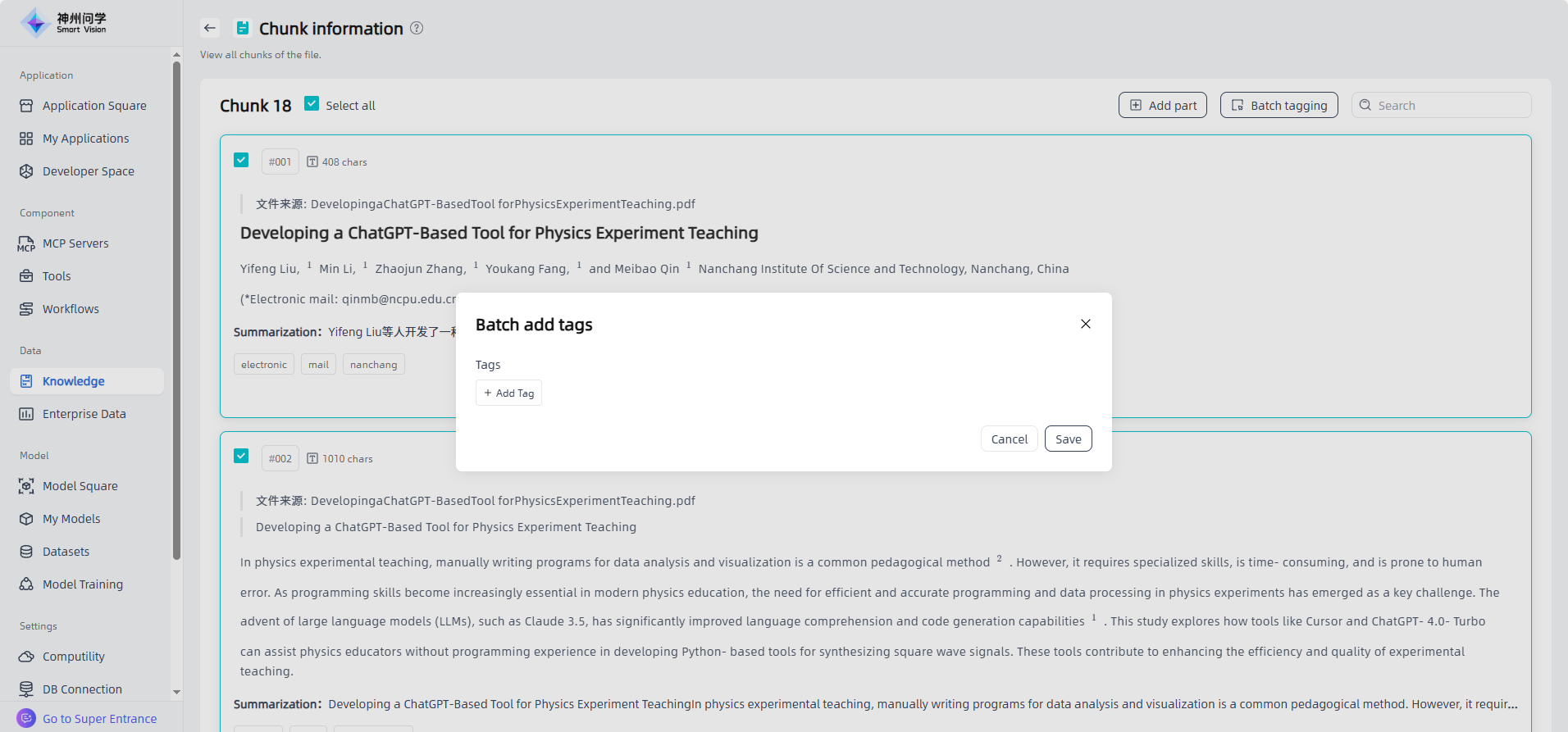
Chunk Tags: For knowledge bases with “Tags” selected in the basic settings, batch tagging is supported for chunks in unstructured documents and FAQ files.

Synchronize external data sources
Start: In "Data - Knowledge", click the "Create Knowledge" button in the upper left corner to enter the "Create Enterprise Knowledge Base" page.
Select knowledge source: Select an existing knowledge source, or click "Add knowledge source" to bind a new knowledge source.
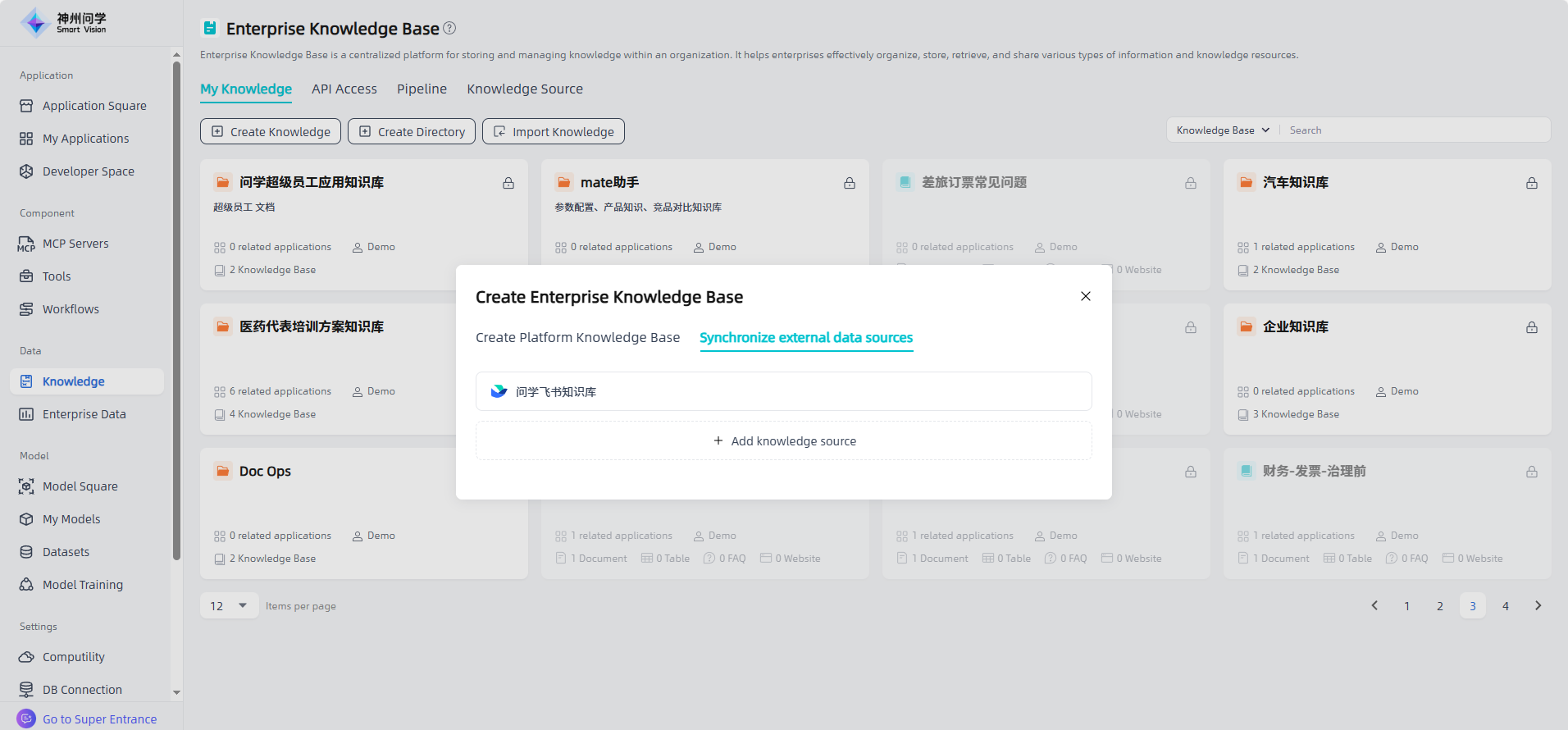
Select knowledge base & settings: Select the knowledge base to be added and set up the knowledge base. Click "Confirm" to complete the synchronization of the external data source and display it in the enterprise knowledge base list.


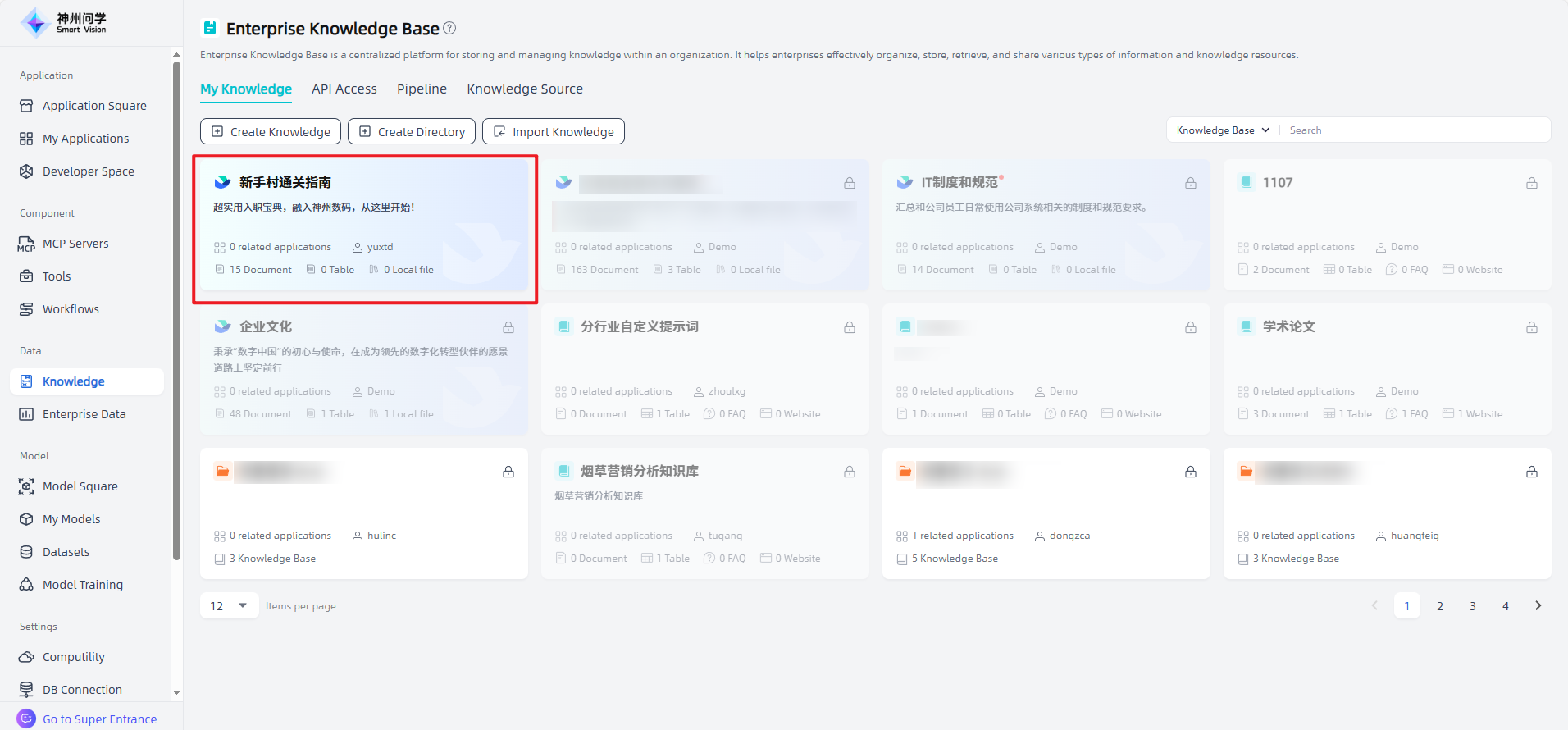
Edit and modify: Click on the knowledge base added through "Synchronize external data sources" to view the files in the knowledge base and support operations such as enabling/disabling/segmented modification. In addition to supporting synchronization of a single file, you can also synchronize all to synchronize the entire database.
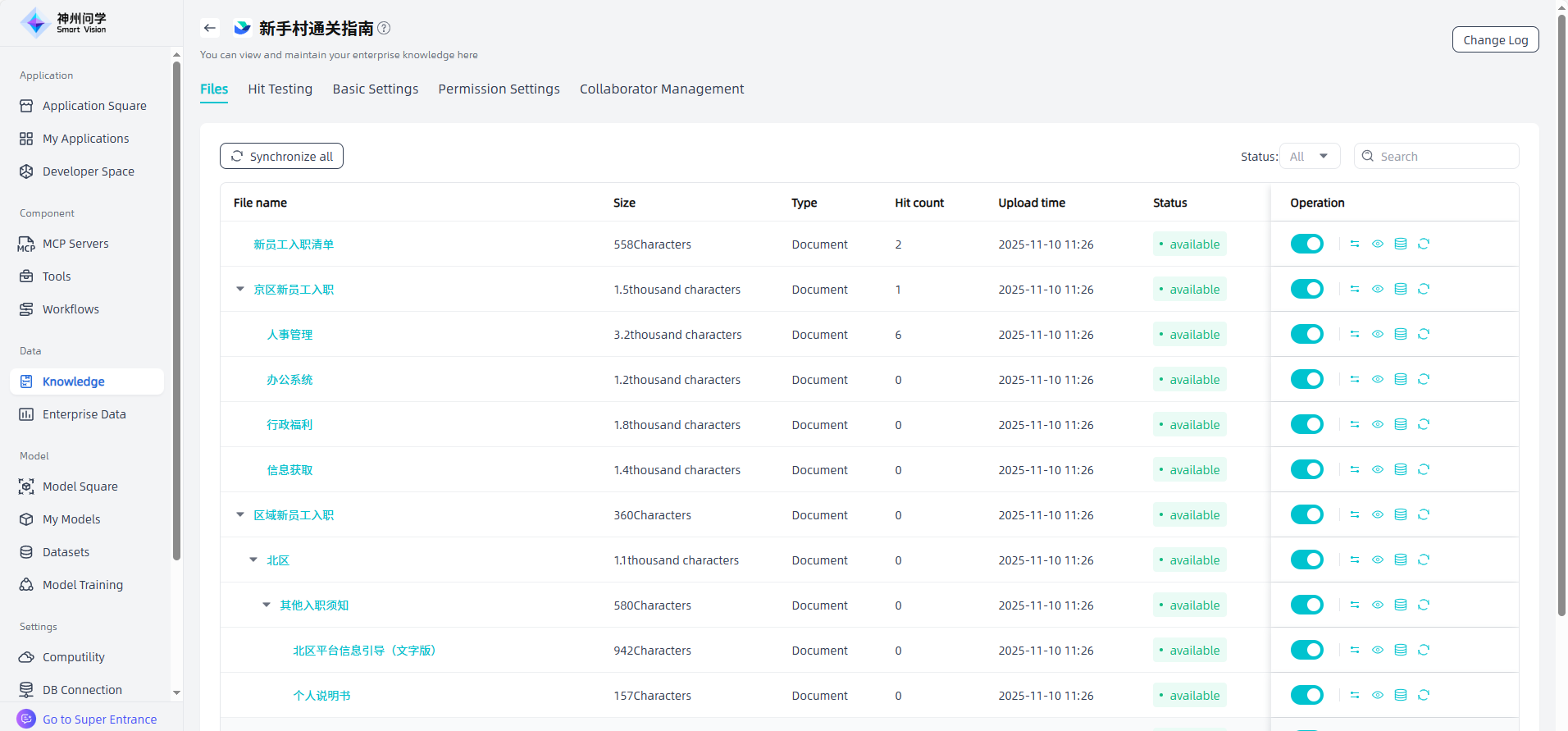
Hit Testing
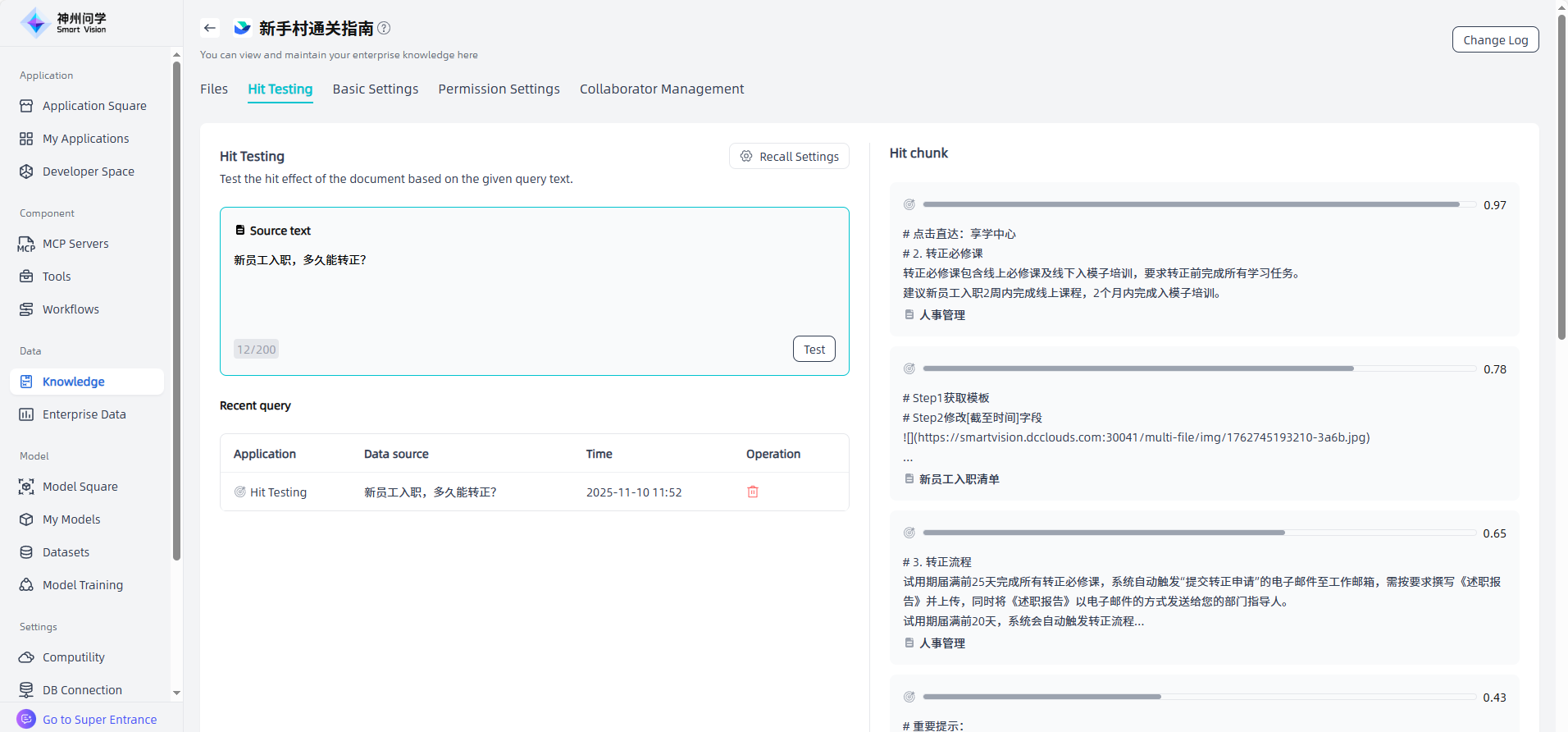
In the Knowledge Base Details - Hit Testing, you can input query text for hit effect testing. You can click on a hit chunk to view its details. Recall settings are supported, allowing you to switch between appropriate models as needed.

Basic Settings
You can modify the knowledge base name, knowledge base description, metadata, index mode, and vector database in the Knowledge Base Details - Basic Settings. After modification, all files of the knowledge base will be executed according to this setting.
Permission Settings
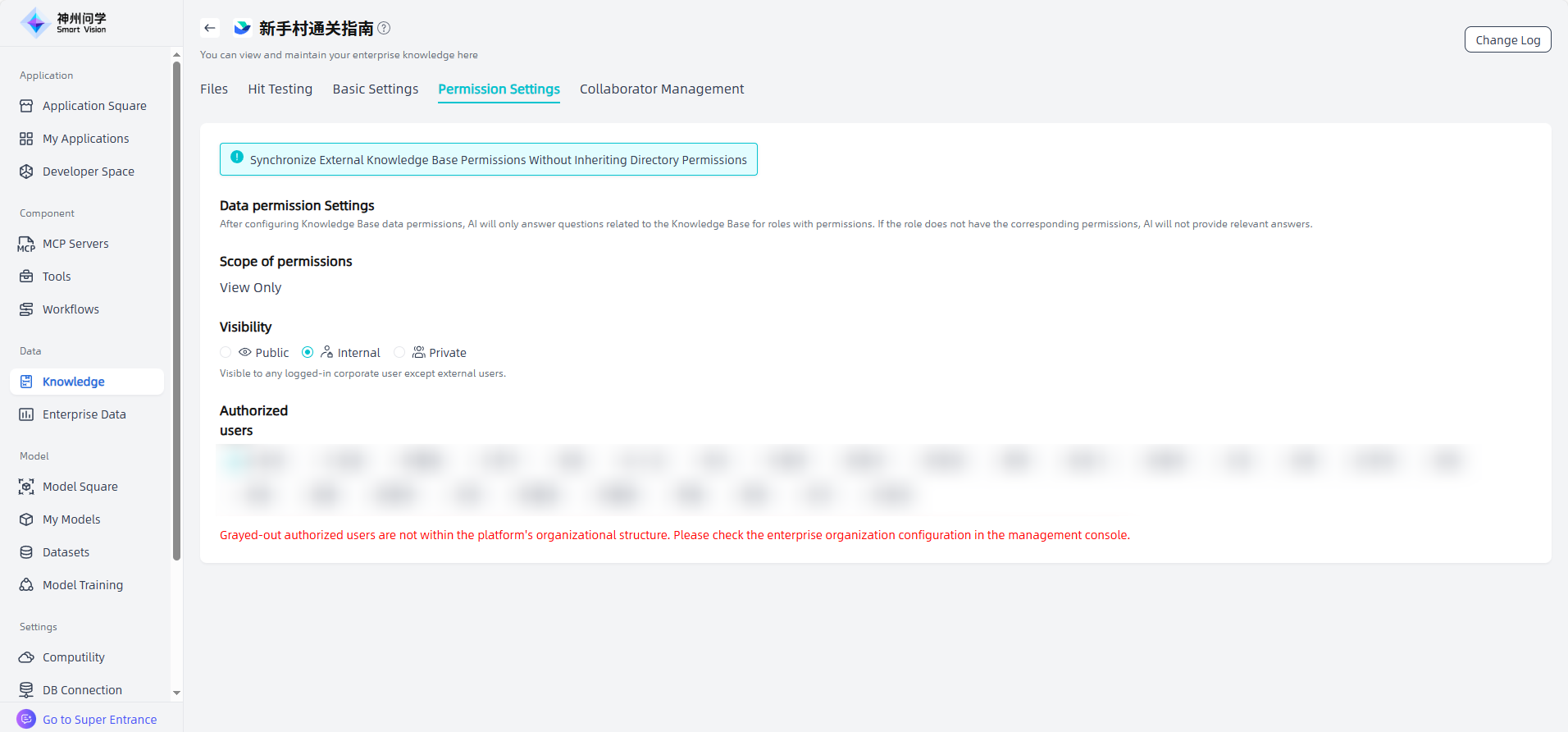
You can set usage permissions in the Knowledge Base Details - Permission Settings, which supports setting three types of permissions: public, internal, and private. After configuring the knowledge base permissions, AI will only answer questions related to the knowledge base for roles with permissions. If the role does not obtain the corresponding permissions, AI will not provide relevant answers.
Collaborator Management
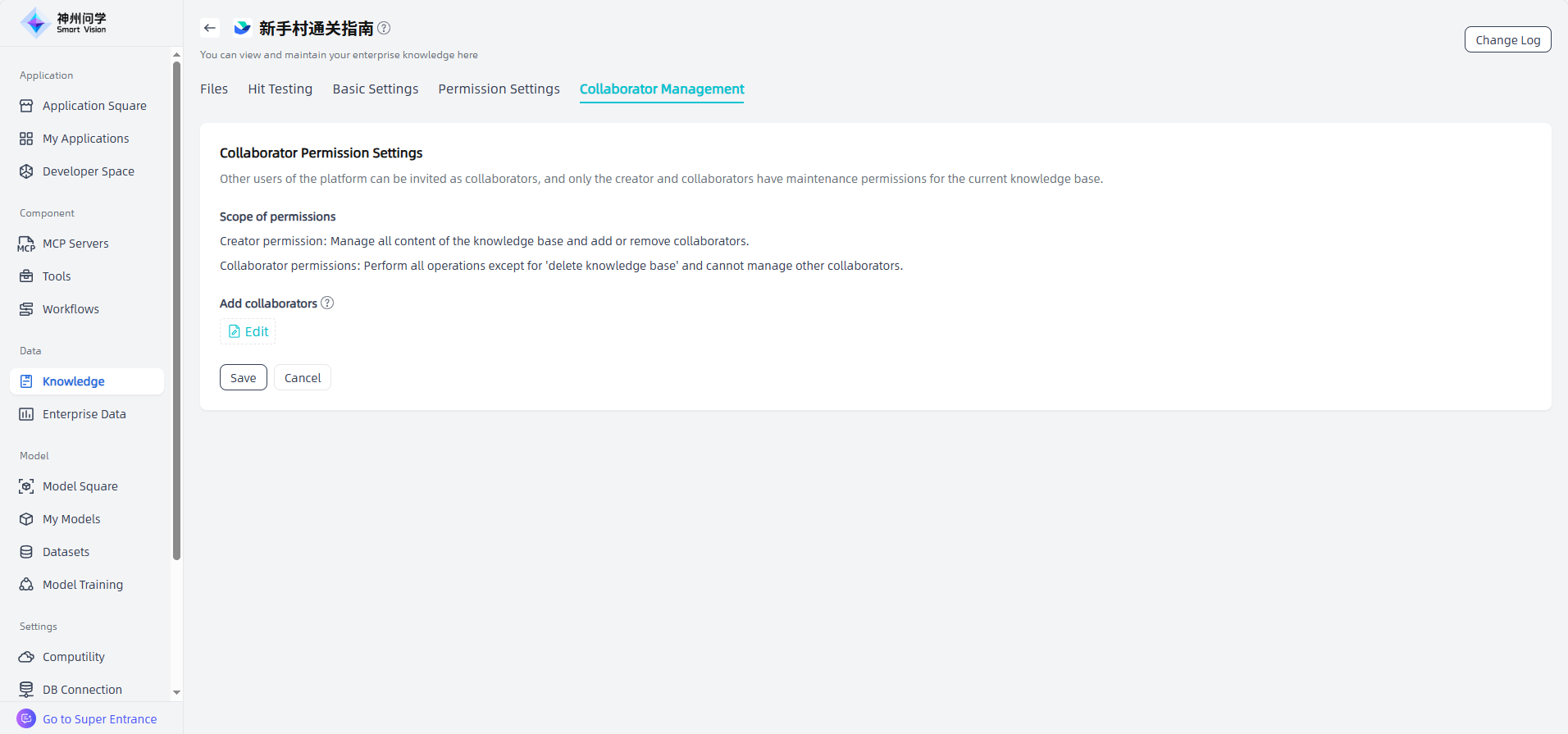
For the knowledge bases you create, you can configure collaborator permissions in Knowledge Base Details - Collaborator Management. You can invite other platform users as collaborators as needed. Only the creator and collaborators have maintenance permissions for the current knowledge base. Users with collaborator permissions can perform all operations except “Delete Knowledge Base”, but they cannot manage other collaborators.
Create Knowledge Base Directory
The Knowledge Base Directory is a collection of enterprise knowledge bases and a structured way of organizing knowledge. It organizes and categorizes knowledge according to specific topics or categories, allowing users to more conveniently find and obtain the required knowledge resources through the knowledge directory.
If you have many knowledge resources or they cover multiple topics, you can first create a knowledge directory in Data - Knowledge, and then create a knowledge base under this knowledge directory. A successfully created knowledge directory will be displayed in Data - Knowledge.
Operation Guide
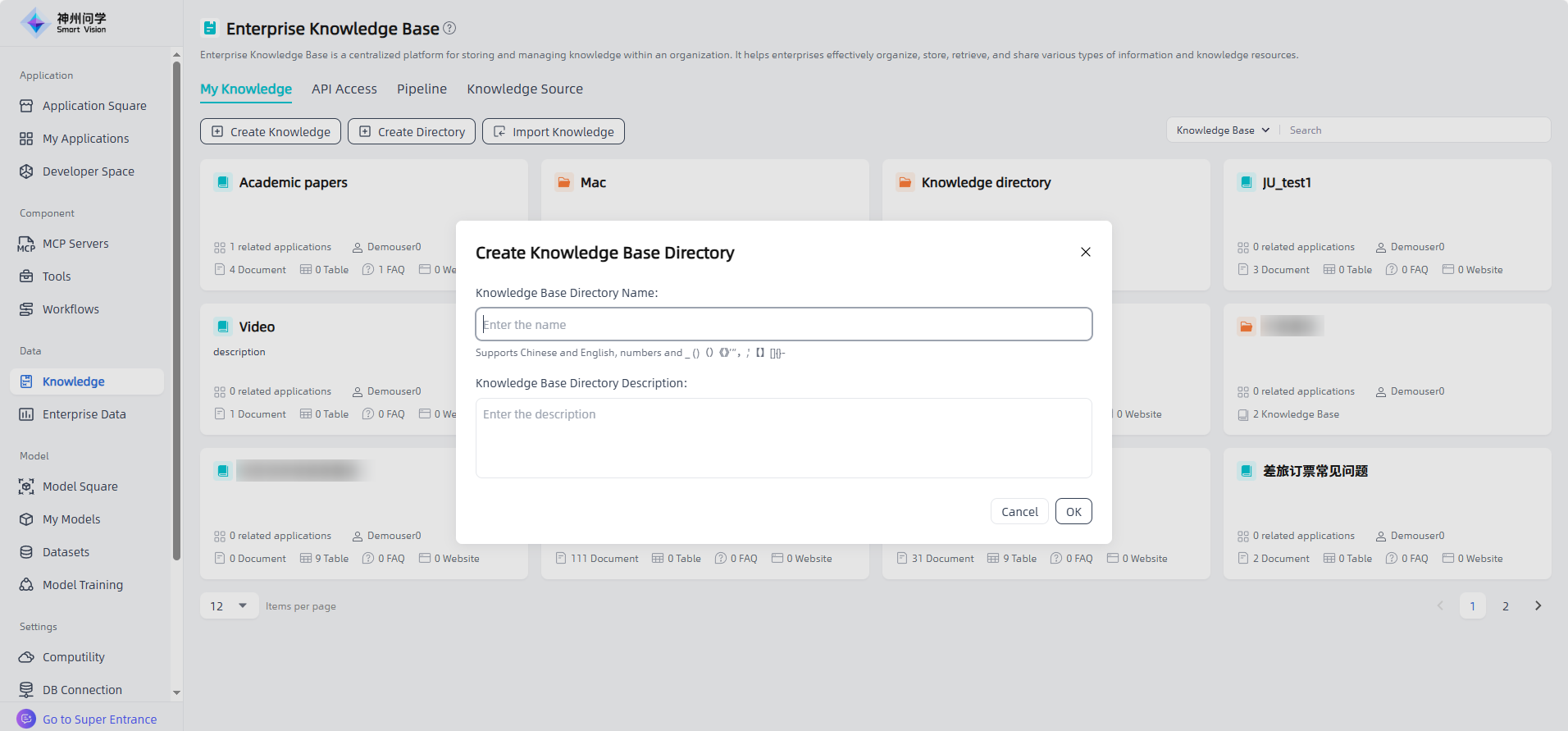
Start: Go to "Data - Knowledge, click the "Create Directory" button in the upper left corner to enter the "Create Knowledge Base Directory" page.
Fill in the Knowledge Base Directory information: fill in the Knowledge Base Directory name and description to start creating the Knowledge Base Directory.
Create enterprise knowledge base: After filling in the knowledge base directory information, enter the knowledge base directory details page and click "Create enterprise knowledge base" (the operation process is the same as directly creating knowledge base).You can view the change history of this knowledge directory through the "Change Log" in the upper right corner.
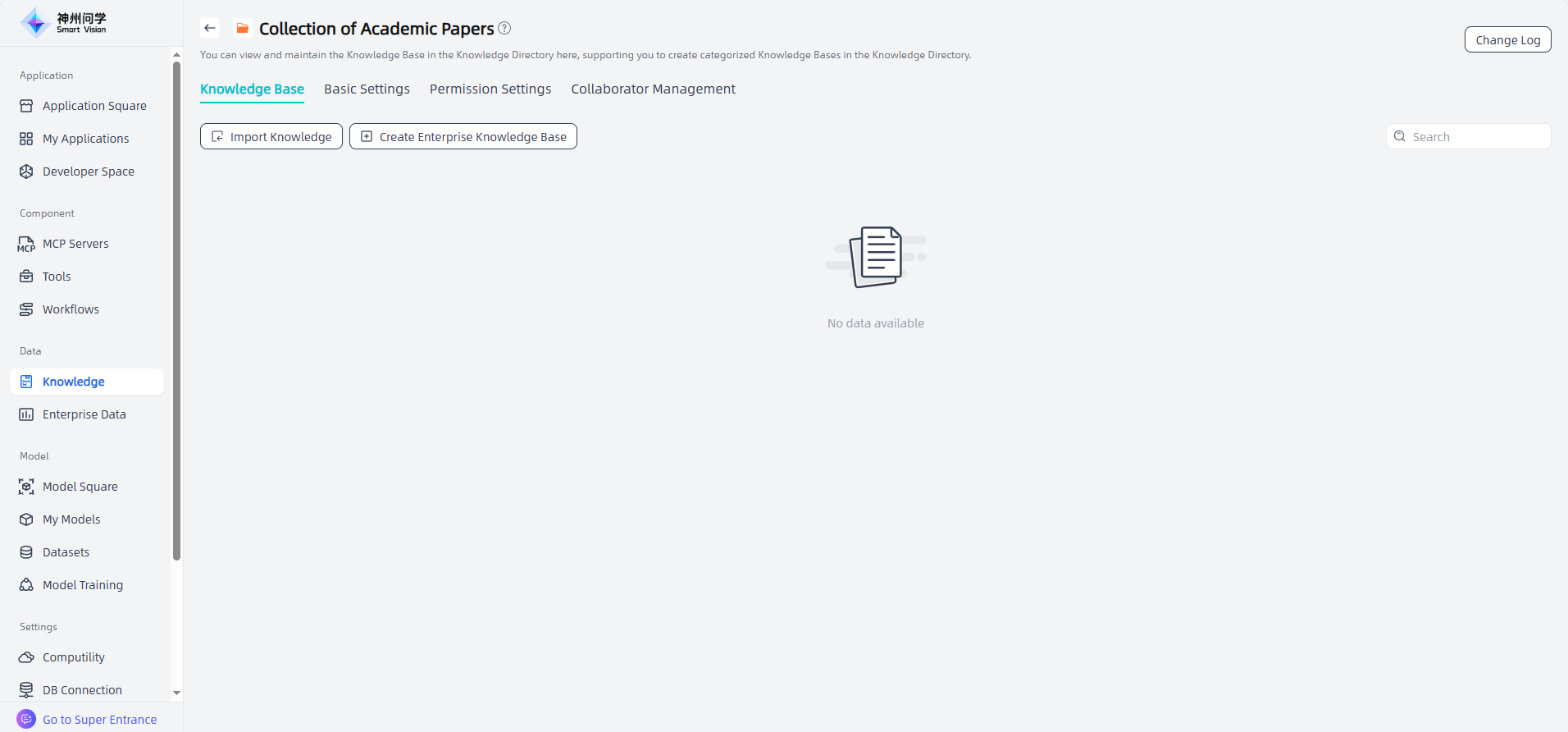
Basic Settings: On the knowledge base directory details page, you can click "Basic Settings" to modify the name and description of the knowledge base directory.
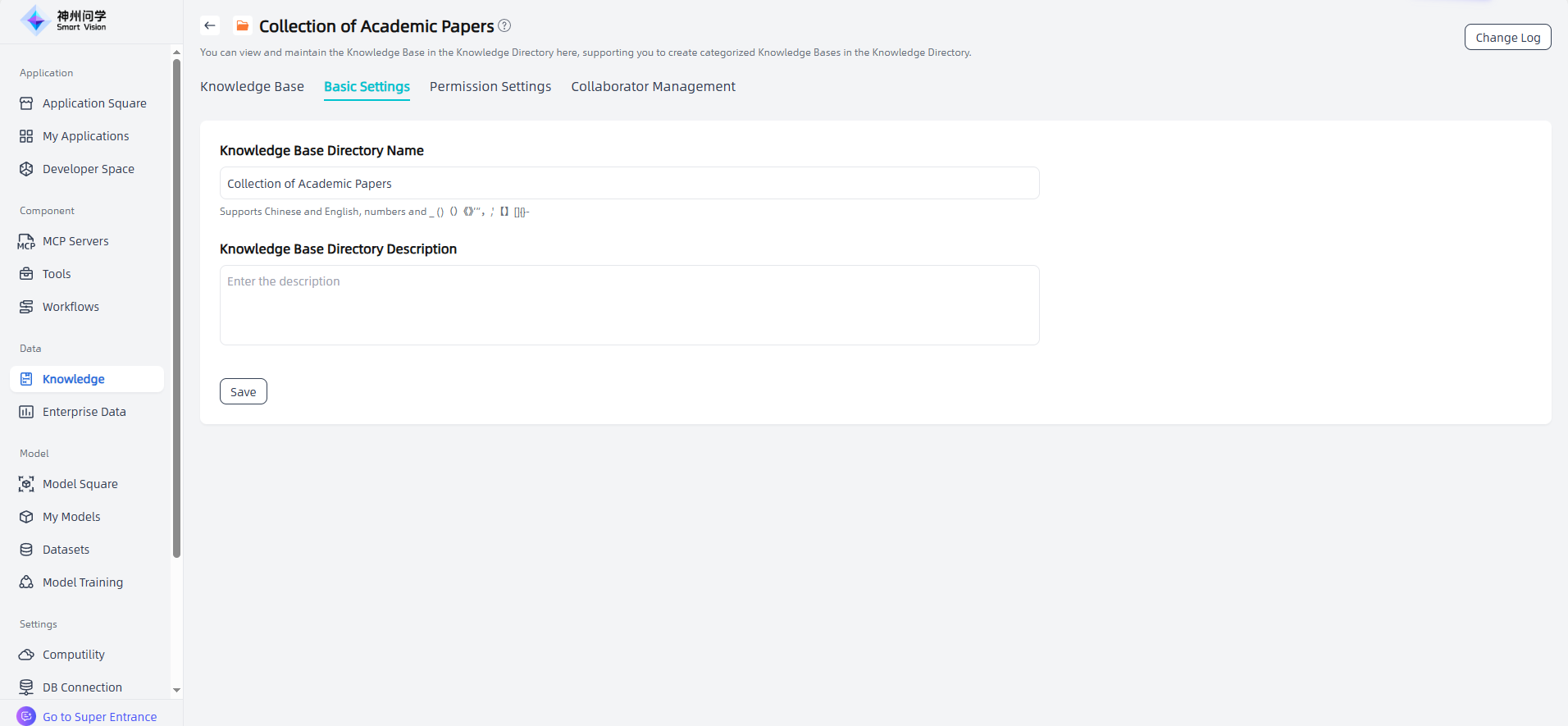
Permission Settings: You can set usage permissions in the Knowledge Base Directory Details - Permission Settings. You can set public, internal, and private permissions and authorize users who can access the knowledge base as needed. After configuring permissions, AI will only answer questions related to the knowledge base directory for roles that have permissions. If the role does not have the corresponding permissions, AI will not provide relevant answers.
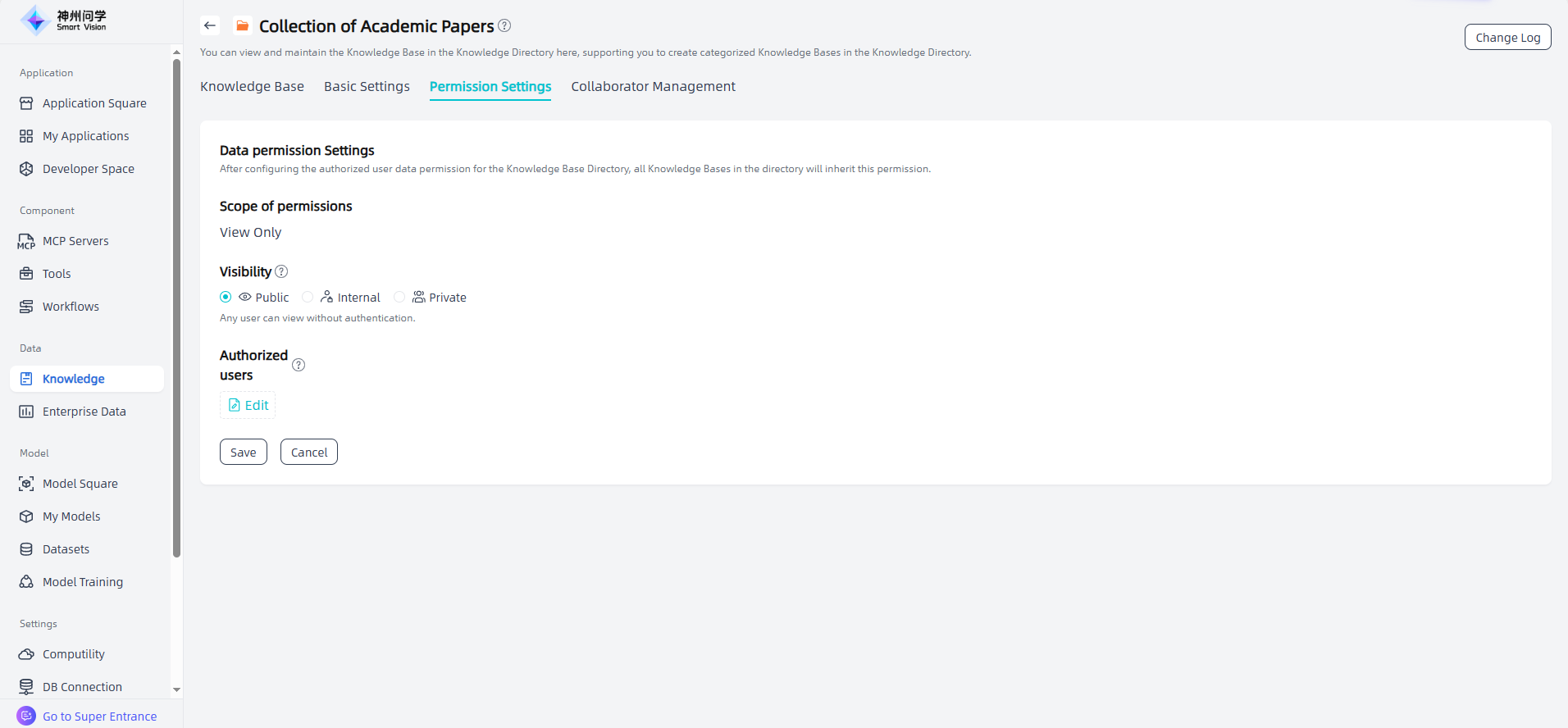
Collaborator Management : For the knowledge bases you create, you can configure collaborator permissions in Knowledge Base Details - Collaborator Management. You can invite other platform users as collaborators as needed. Only the creator and collaborators have maintenance permissions for the current knowledge base. Users with collaborator permissions can perform all operations except “Delete Knowledge Base”, but they cannot manage other collaborators.
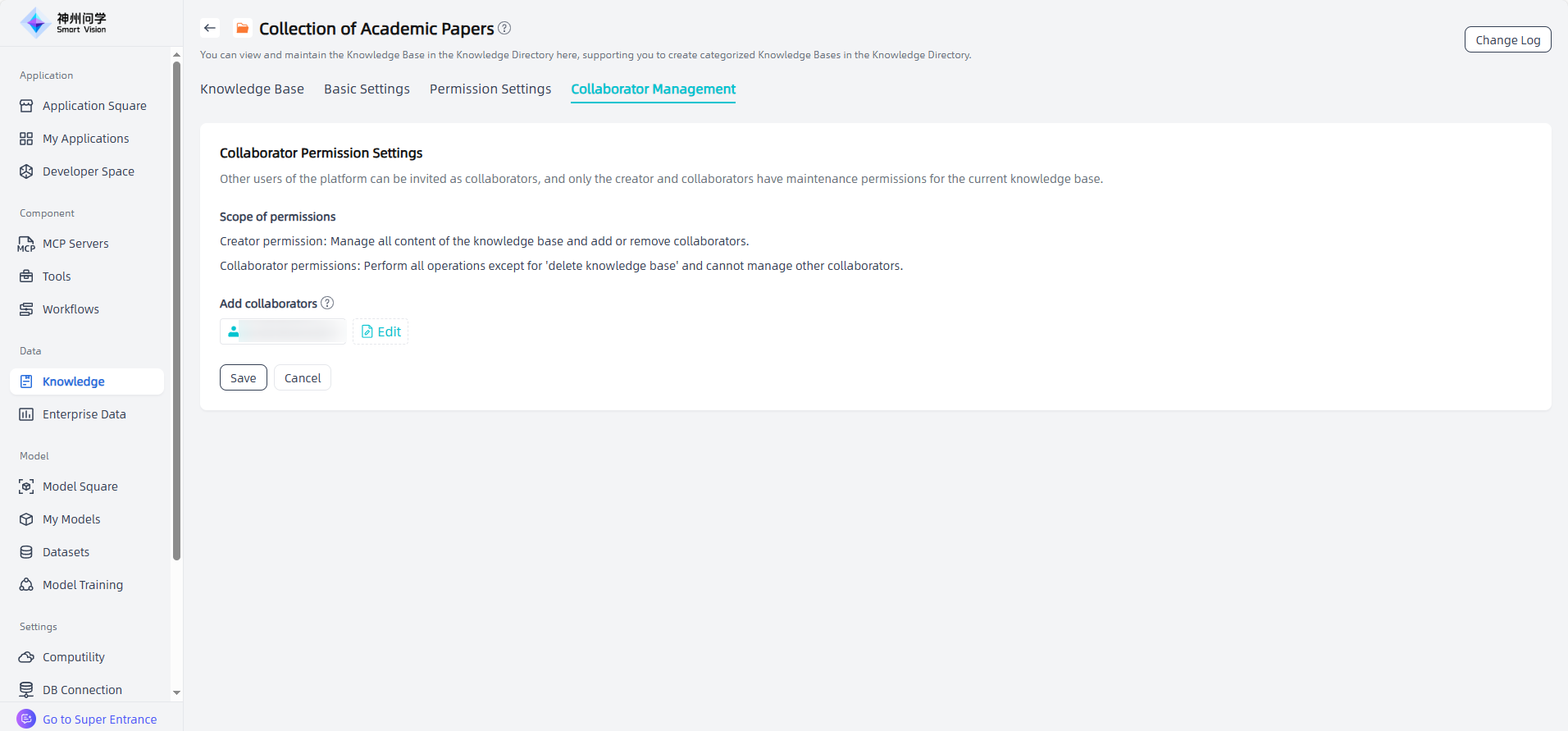
The collaborators configured in the knowledge directory will be inherited by all knowledge bases under this directory. Collaborators inherited from the knowledge directory cannot be removed at the knowledge base level.

Import Knowledge Base
In Data - Knowledge, click the "Import Knowledge" button in the upper left corner to directly import existing compressed knowledge base files and execute governance according to the knowledge base configuration. The imported knowledge base will be displayed in "My Knowledge" for you to use directly or make adjustments based on it. For the imported knowledge base, its modification, setting, and hit testing are the same as "Create Knowledge Base".

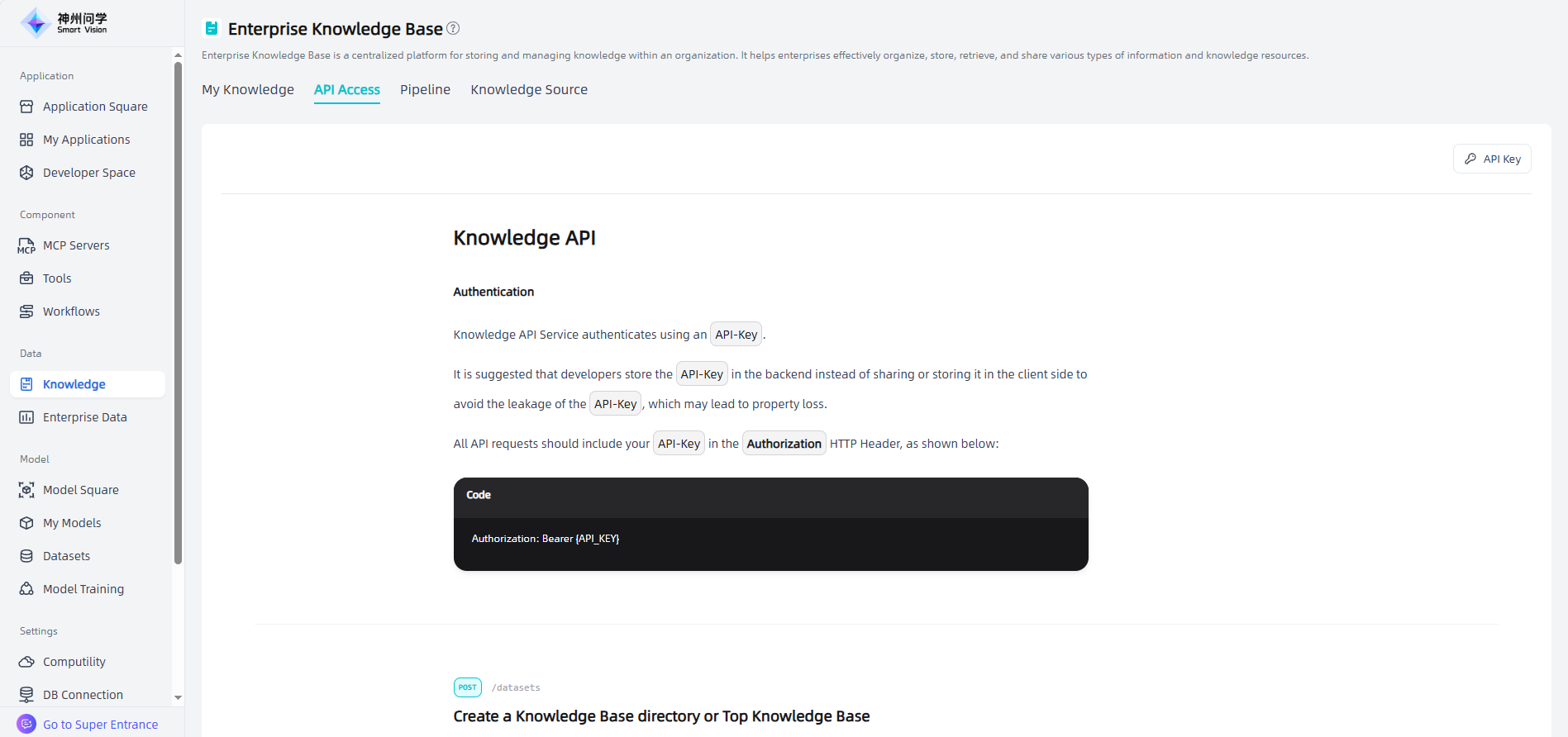
API Access
In Data - Knowledge, click on the "Access API" tab to view the API access methods for the enterprise knowledge base. The enterprise knowledge base access API supports authorization key management, and API keys are required to call the API (click the "API Key" button to create an API key).
Pipeline
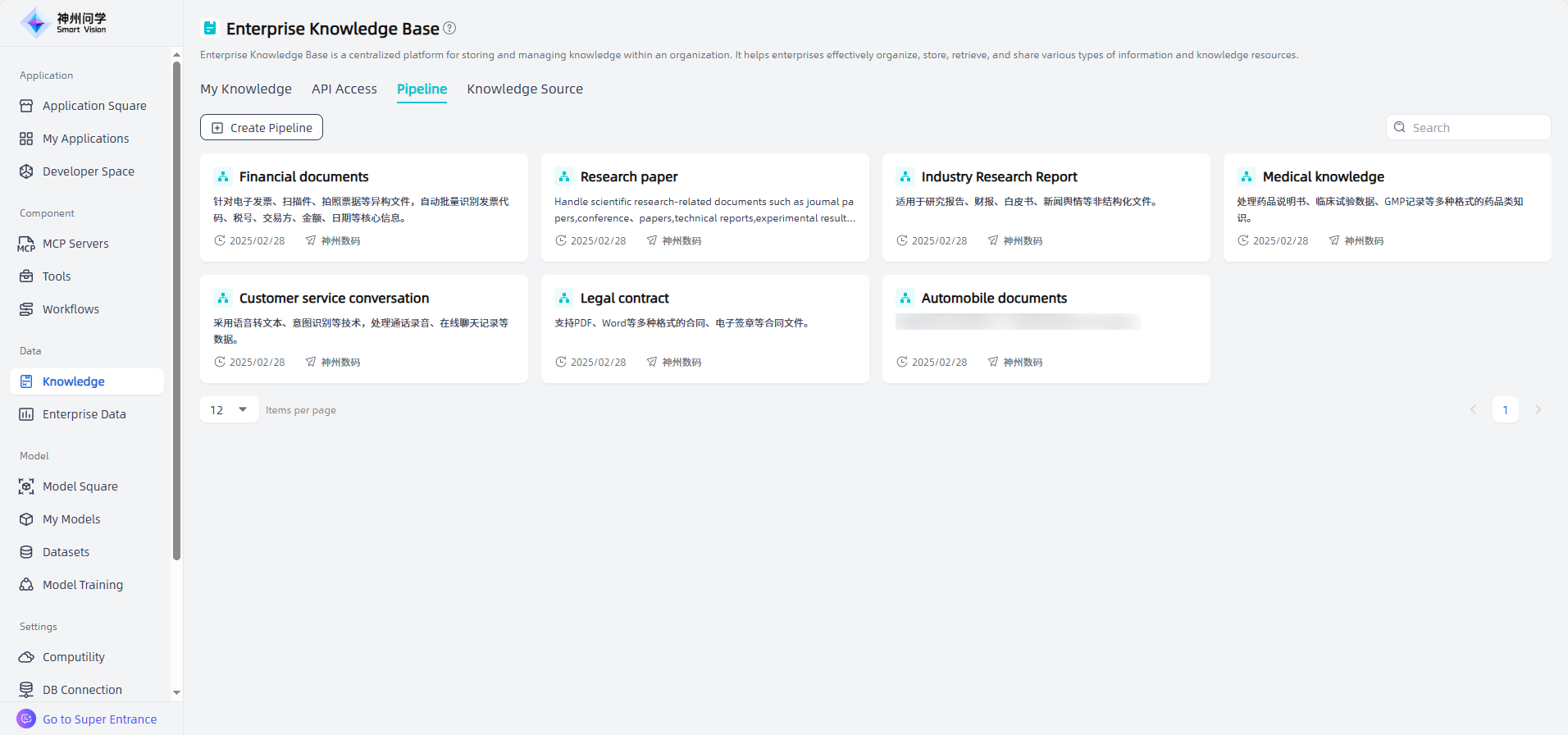
Data - Knowledge - Pipeline displays all available knowledge governance templates, including those pre-set on Smart Vision and those created by yourself, for users to use in Create Platform Knowledge Base - Add governed file - Select pipeline.
Clicking on a pipeline allows you to view configuration details, edit and modify as needed, or click "To Experience" to experience the effect of the pipeline. If you modify the configuration during the experience, the system will prompt you to update the pipeline as needed.

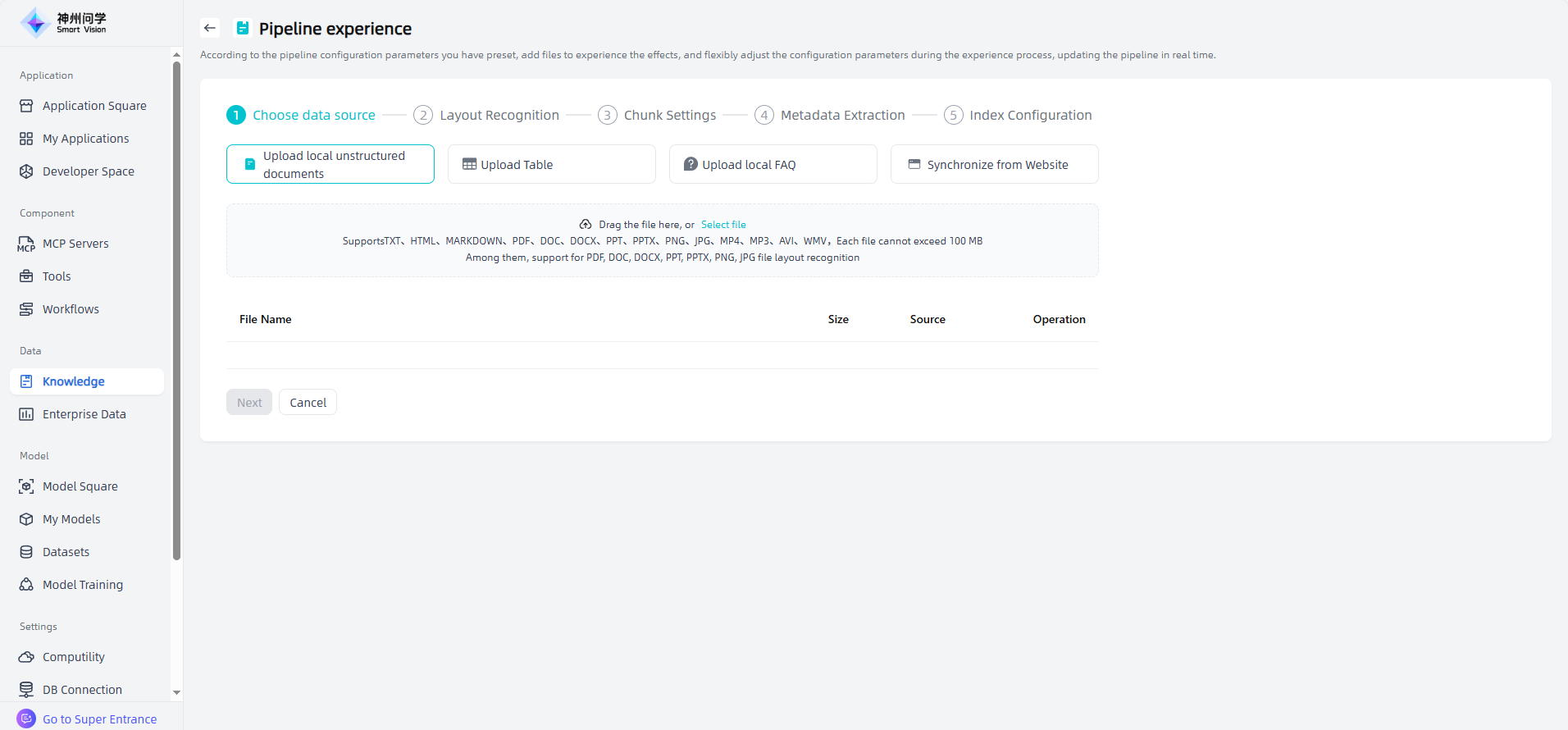
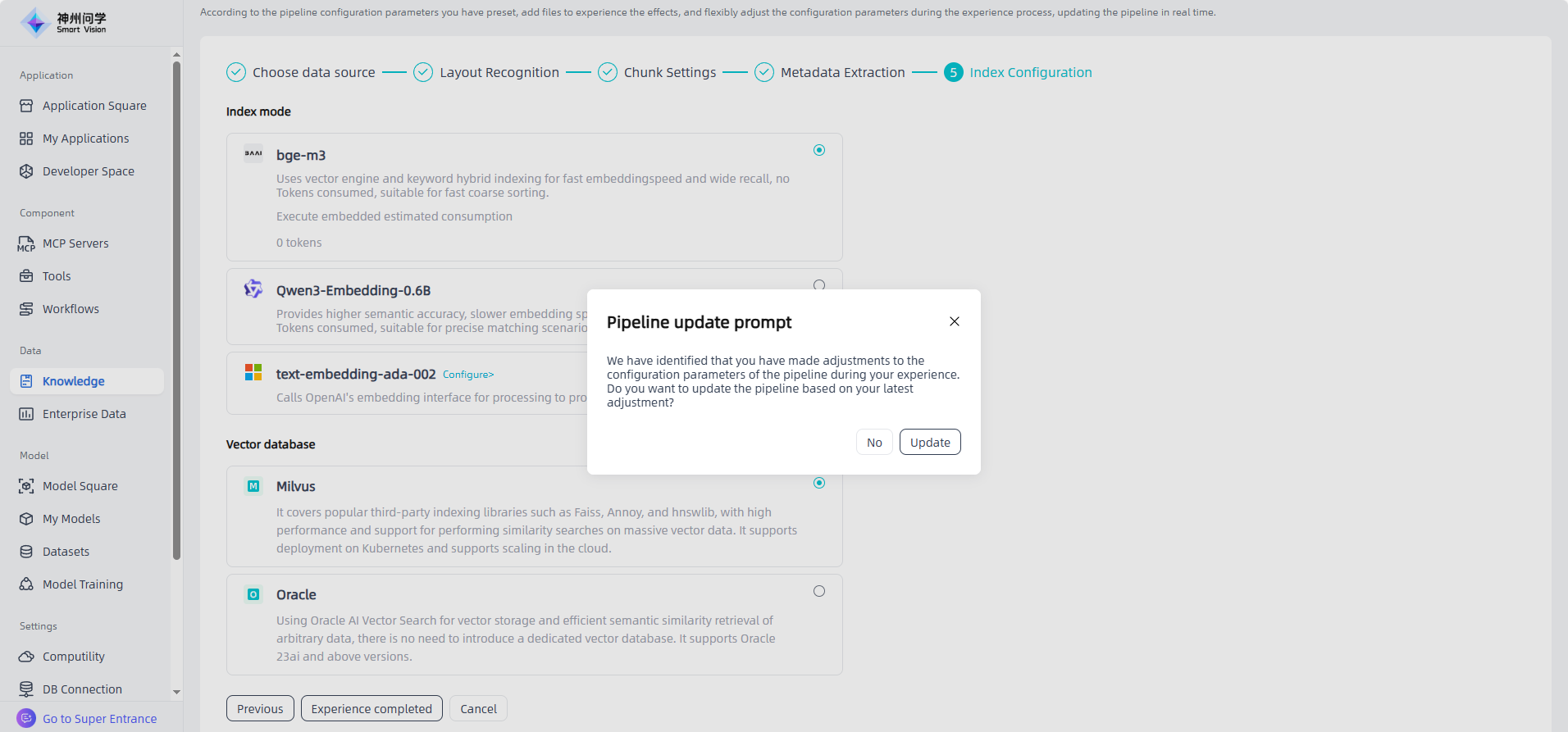
Click the "Create Pipeline" button in the upper left corner to create a pipeline as needed, and click "To Experience" to experience the effect of the newly added pipeline. Click "Save" to complete the pipeline creation.
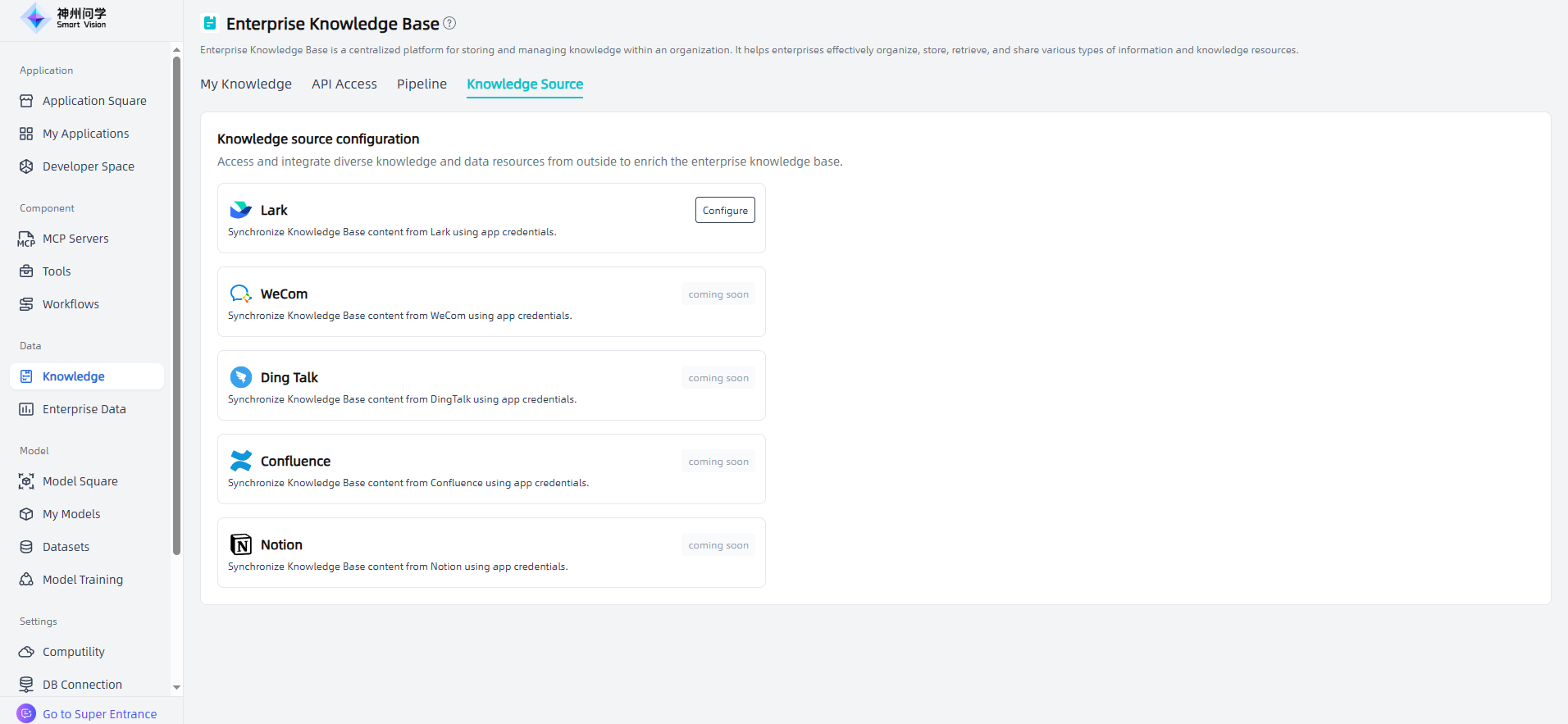
Knowledge Source
Smart Vision supports accessing and integrating diverse external knowledge data resources to enrich the enterprise knowledge base. Smart Vision currently supports synchronizing knowledge base content from Lark through Lark application credentials.
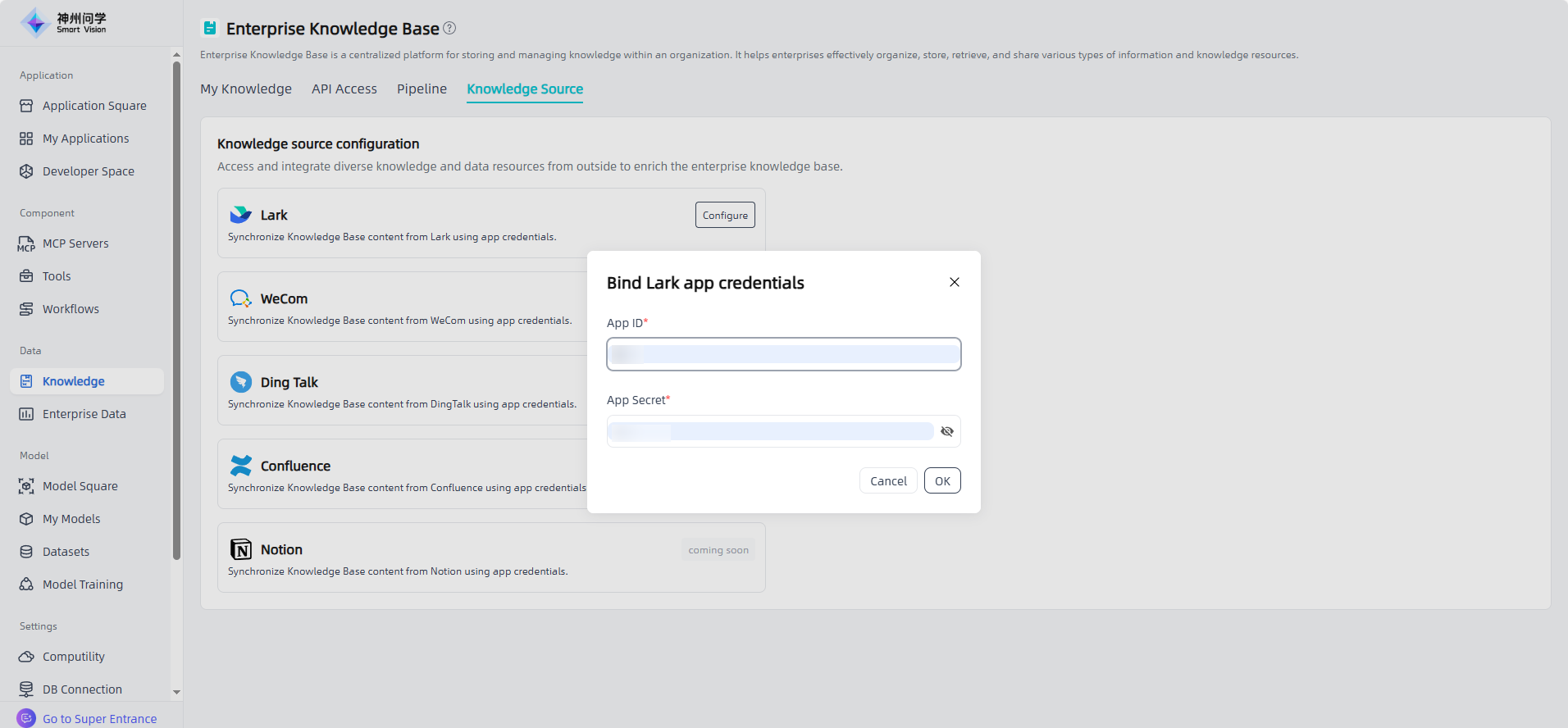
After clicking "Configure", fill in the Lark application credential information to bind the Lark application, and "Bound" will be displayed in the knowledge source configuration.
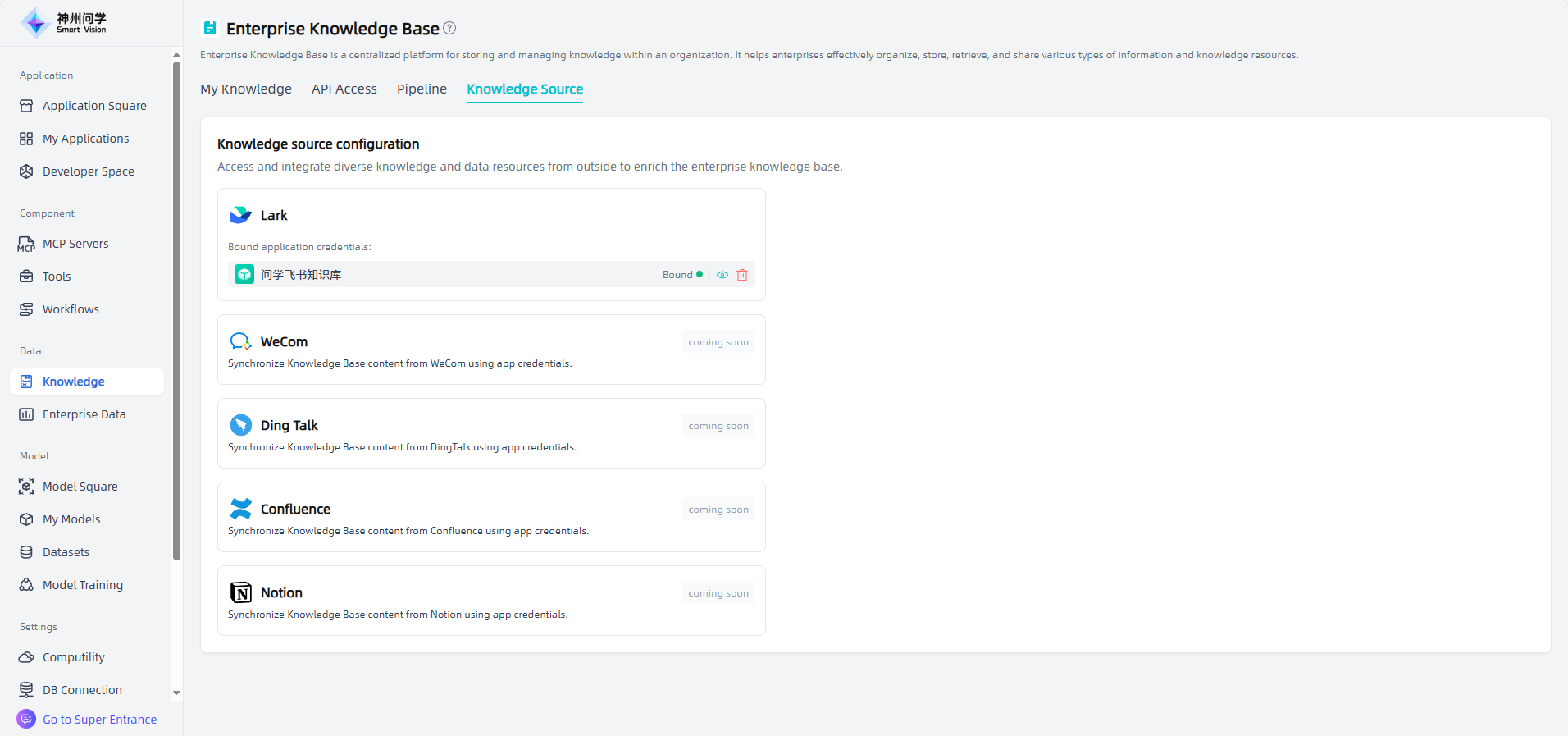
The newly bound Lark application will appear in the "Create Knowledge Base-Synchronize External Data Source" list (For details: Create Knowledge Base), making it easy to select synchronization as needed.
